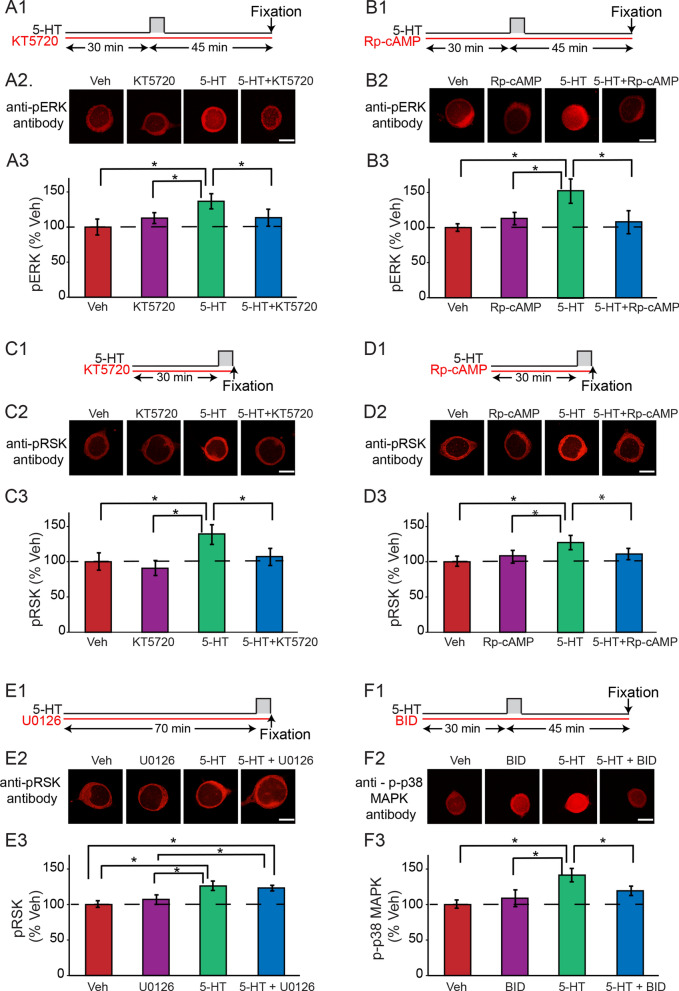
Figure 2.
The interactions between PKA and ERK (A,B), PKA and RSK (C,D), RSK and p38 MAPK (E). A1, Protocol for applying the PKA inhibitor KT5720 with 5 min 5-HT. A2, Representative confocal images of pERK in SNs at 45 min post-onset of 5-HT, in the absence or presence of KT5720. A3, Summary data. KT5720 significantly decreased pERK induced by 5-HT (n = 10). B1, Protocol for applying the PKA inhibitor Rp-cAMP with 5-HT. B2, Representative confocal images of pERK at 45 min post-onset, in the absence or presence of Rp-cAMP. B3, Summary data. Rp-cAMP significantly decreased pERK induced by 5-HT (n = 6). C1, Protocol. C2, Representative confocal images of pRSK immediately after 5-HT, in the absence or presence of KT5720. C3, Summary data. KT5720 significantly decreased pRSK induced by 5-HT (n = 7). D1, Protocol. D2, Representative confocal images of pRSK immediately after 5-HT, in the absence or presence of Rp-cAMP. D3, Summary data. Rp-cAMP significantly decreased pRSK induced by 5-HT (n = 9). E1, Protocol for applying the MEK inhibitor U0126 with 5-HT. E2, Representative confocal images of pRSK immediately after 5-HT, in the absence or presence of U0126. E3, Summary data. U0126 did not significantly attenuate the increase of pRSK immediately after 5-HT (n = 6). F1, Protocol for applying the RSK inhibitor BI-D1870 (BID) with 5-HT. F2, Representative confocal images of p-p38 MAPK at 45 min post-onset of 5-HT, in the absence or presence of BID. F3, Summary data. BID attenuated the induction of p-p38 MAPK 45 min post-onset of 5-HT (n = 9). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. All scale bars are 40 μm. *p < 0.05.