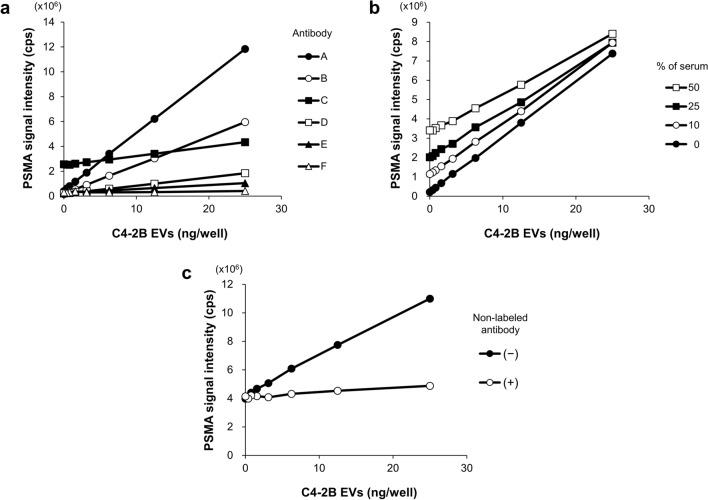
Figure 2.
Determination of the optimal conditions for the plate-based PSMA-EV sandwich ELISA. EVs isolated by sequential centrifugation from culture medium of C4-2B cells (C4-2B EVs) were used as a positive control for PSMA-expressing EVs. Samples were applied to a well of 96-well plate coated with Tim4. After washing, ALP-labeled anti-PSMA antibody was added to the well, followed by detection of chemiluminescence in the presence of ALP substrate. (a) Antibody selection. Commercially-available anti-PSMA antibodies (A: Miltenyi Biotec, REA408; B: BioLegend, LNI-17; C: MBL, 107-1A4; D: Abcam, GCP-05, E: R&D, sheep-polyclonal; F: Millipore, 3/A12) were labeled with ALP. The PSMA-EV levels in samples containing increasing doses of C4-2B EVs (0, 0.39, 0.78, 1.56, 3.13, 6.25, 12.5, and 25 ng/well in 50 µL) were determined. (b) Matrix effect on sandwich ELISA. Measurement of the PSMA-EVs in C4-2B EVs was performed in the presence of increasing concentration of pooled serum from 6 normal donors (0, 10, 25, and 50%). (c) Competitive sandwich ELISA. Measurement of the PSMA-EVs in pooled serum containing increasing doses of C4-2B EVs (50 µL) was performed in the presence and absence of an excess amount of non-labeled anti-PSMA antibody (fivefold).