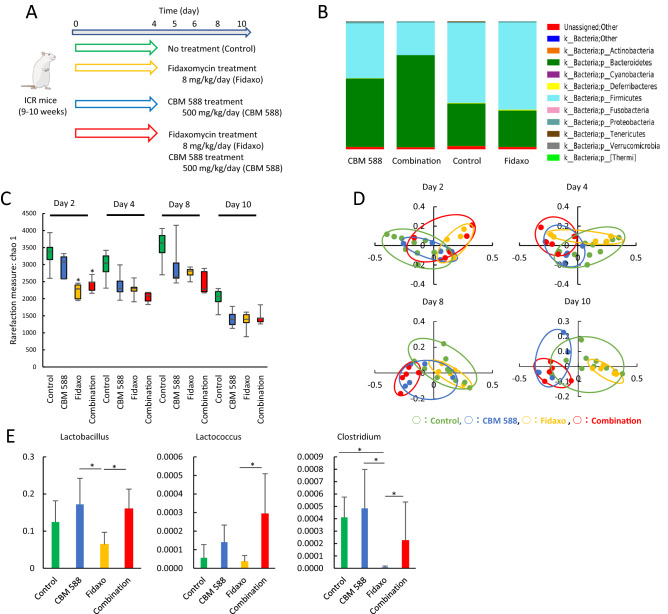
Figure 2.
C. butyricum modulated the gut microbiome composition under fidaxomicin treatment and increased Lactobacillus spp. and Lactococcus spp. (A) Experimental design for gut microbiome analysis with 9- to 10-week-old ICR Swiss mice. (B) Bacterial compositions in different experimental groups at the phylum level. All values are mean (n = 5). (C) Comparison of the Shannon index of different groups. The box and whiskers represent the smallest and largest values, with the median in the center of each box (n = 5). (D) Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) based on weighted Unifrac distances among CBM 588 monotherapy group (CBM 588), fidaxomicin monotherapy group (Fidaxo), and combination group (Combination). (E) Effect of fidaxomicin and/or CBM 588 administration on relative species abundance (≥ 0.001%) in the fecal samples. After quality filtering steps, three species (Lactobacillus spp., Lactococcus spp., and Clostridium spp.) were considered to have significantly higher relative abundance (%) in the combination group, compared with the fidaxomicin administration group at day 8. Data represent the mean values of relative abundances ± SD (n = 5–10).