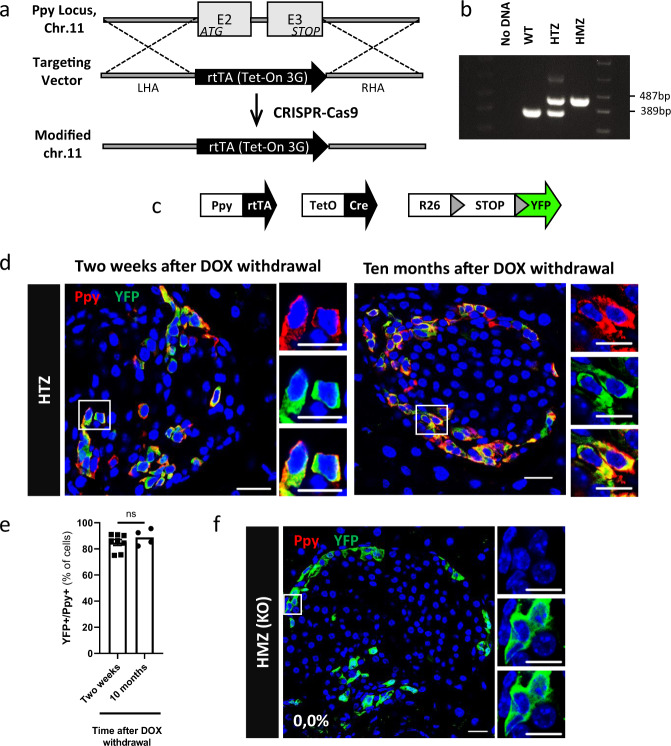
Fig. 1. Generation of knock-in mice to lineage-trace γ-cells and inactivate the Ppy gene.
a CRISPR-Cas9 was used to replace the Ppy coding sequence (E2, E3: exons 2 & 3) on mouse chromosome 11 by the rtTA coding region (“targeting vector”). LHA left homology arm, RHA right homology arm. b PCR products of wild-type (WT), Ppy-rtTA heterozygous (HTZ) and Ppy-rtTA homozygous (HMZ) mice (WT band: 389 bp; KI band: 487 bp). “No DNA” is a negative control. Samples derive from the same experiment run at once in one gel. c Transgenes required for tracing the lineages of Ppy-expressing γ-cells. d Ppy+ cells are efficiently YFP-labeled two weeks or 10 months after DOX withdrawal in Ppy-YFPi mice. e Quantification of the YFP-labeled Ppy-expressing cells two weeks (84.9 ± 0.0, n = 8 mice, 5411 Ppy+YFP+ out of 6389 Ppy+ cell scored) or 10 months (88.8 ± 0.0%, n = 4 mice, 2852 Ppy+YFP+ out of 2889 Ppy+ cells scored) after DOX withdrawal. Data are shown as mean±s.e.m; two-tailed Mann–Whitney test (P value 0.4606). f Ppy production is abrogated in Ppy-rtTA homozygous (HMZ, KO) mice: none of the YFP-labeled cells in DOX-treated animals (Ppy-YFPi, Ppy-rtTA HMZ) produces the peptidic hormone (n = 3 mice; 0 Ppy+ out of 1310 YFP+ cells scored). Ppy (red) and YFP (green). Scale bars: 20 μm (10 μm in insets). Region of the pancreas: Ventral. Source data are provided as Source Data file (Supplementary Table b).