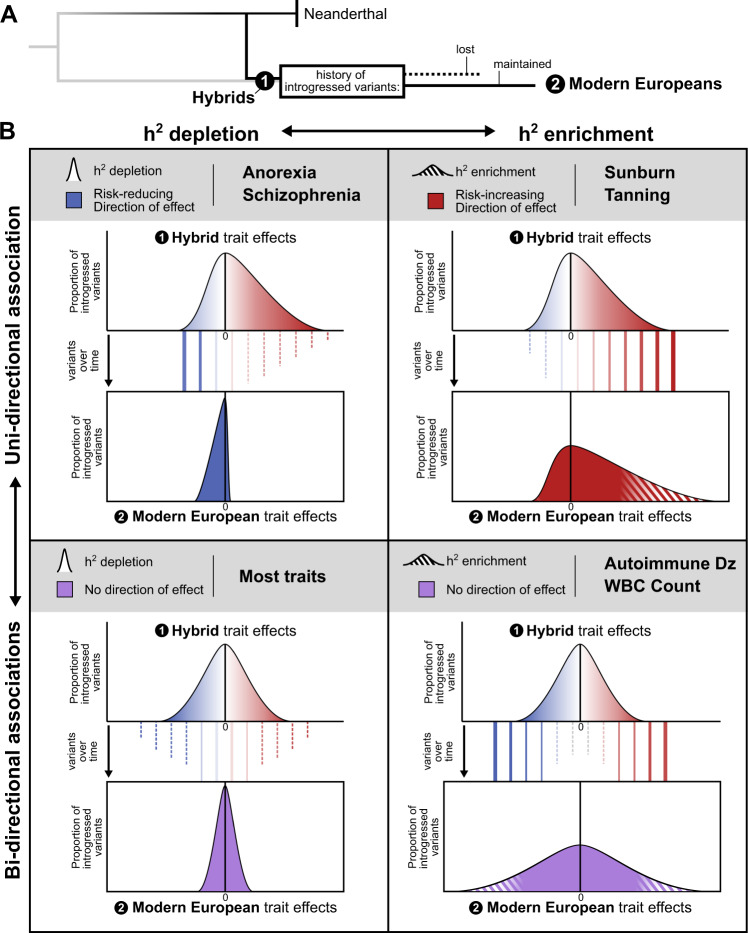
Fig. 5. Patterns of heritability and direction of effect suggest contrasting selective pressures on introgressed variation associated with different traits.
A After admixture, many Neanderthal variants segregated in hybrid populations. As these populations evolved into modern Eurasians, some introgressed variants were lost due to drift or negative selection (dashed line) and some were maintained due to drift or positive selection (solid line). B With regards to introgressed variants in modern Europeans, traits fall into four general quadrants on the axes of heritability enrichment vs. depletion (x-axis) and uni-directional vs. bi-directional trait effects (y-axis). For each quadrant, we depict potential variant histories and selective pressures leading to the observed distribution of introgressed variants’ trait effects (solid and dashed lines). (Bottom Left) Heritability for most traits is depleted among introgressed variants (narrow effect distribution with most variants conferring no effect) with no bias in the direction of effect (centered at zero). This suggests selection against introgressed variants that influenced these traits. (Top Right) The opposite pattern is observed in traits such as sunburn and tanning. These traits are enriched for heritability among introgressed variants (thick tail with more variants conferring trait effects than expected), and they have a bias in their direction of effect (skewed). This pattern suggests that introgression introduced some functional alleles that were positively selected in AMHs. (Bottom Right) Traits, like autoimmune disease risk and white blood cell (WBC) count, have heritability enrichment among introgressed variants (thick tails with many variants conferring trait effect), but no directional bias (centered). In this case, introgression likely contributed increased diversity relevant to the trait—both trait-increasing and -decreasing—into AMHs that was beneficial as they adapted to non-African environments. (Top Left) Finally, traits like anorexia and schizophrenia, show depletion for heritability among introgressed variants (narrow distribution), but they have a significant directionality bias in the few introgressed variants with effects (skewed). This pattern could be produced by negative selection purging most introgressed alleles that influence the trait paired with selection for a small number of introgressed beneficial alleles.