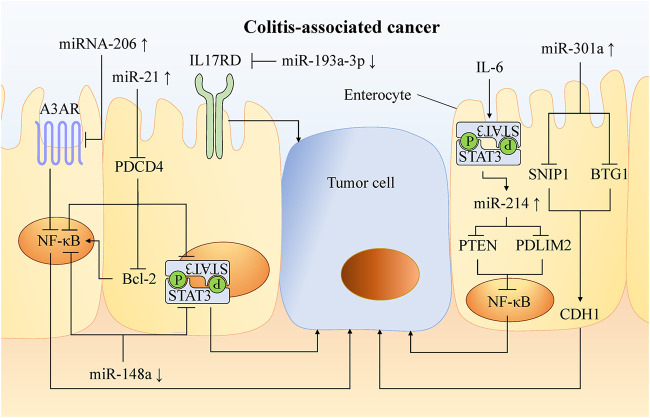
FIGURE 3.
Mechanism of miRNA involved in carcinogenesis of UC. In UC, chronic activation of carcinogenic pathways such as NF-κB and STAT3 leads to a higher risk of CAC. A variety of miRNAs can promote or inhibit the occurrence of cancer by targeting molecules in these pathways. Increasing the abundance of anti-oncogenic miRNAs and decreasing the abundance of oncogenic miRNAs can inhibit tumor formation and progression in experimental colitis. This provides a new therapeutic target for the preventing and treatng CAC.