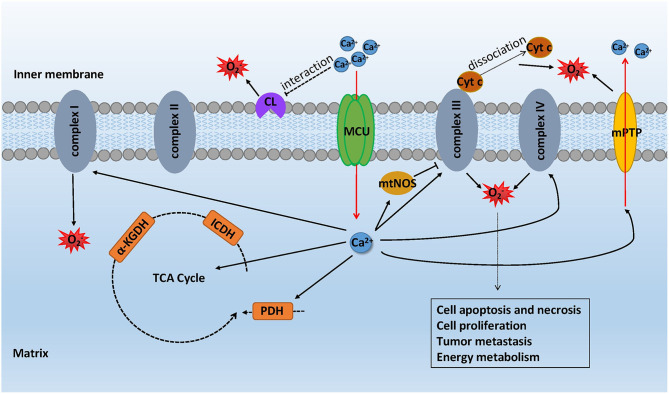
Figure 3.
mROS formation mediated by MCU-dependent calcium uptake. With the stimulation of oxidative stress, the elevated mCa2+ took up by MCU interrupts energy metabolism causing the generation of mROS while the mROS formation can impact the cell metabolic function in turn. mCa2+ increases the activity of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH), pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH), and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) in the TCA cycle, thus promoting mROS production. mtNOS, activated by mCa2+, hampers the conduction of electron, making complexes I and III generate mROS. mPTP opening results in the rupture of the outer membrane and thus causing the release of cytochrome c. Overloaded mCa2+ has an effect on Ca2+-CL binding, inducing the reorganization of membrane components, which causes the high-rate generation of mROS at the ubiquinone level.