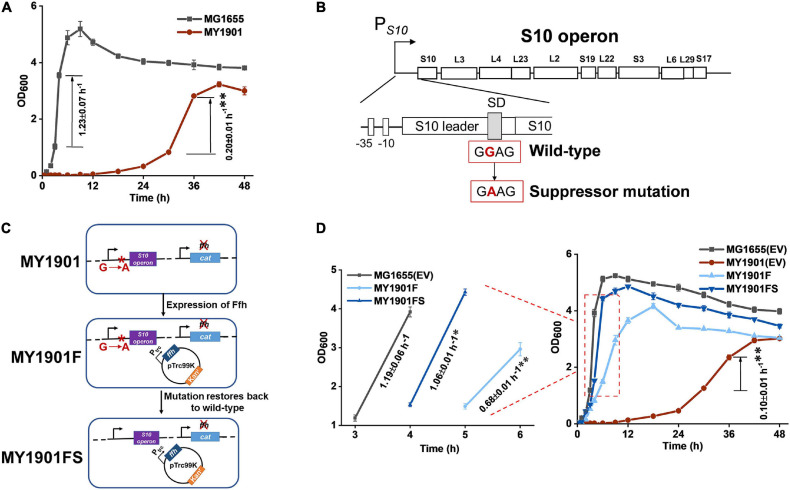
FIGURE 1.
Identification of SRP suppressor strain and its growth. (A) Growth curves and growth rates of the wild-type strain MG1655 and the suppressor strain MY1901. (B) The suppressor mutation sites in the SD sequence of S10 operon. The region and encoded ribosomal proteins of the S10 operon are shown. The wild-type SD sequence (GGAG) mutated into suppressor mutation (GAAG). (C) Restoration of the wild-type allele. Plasmid pTrc99K-Ffh was first transformed into strain MY1901, generating the strain MY1901F. Ffh protein was produced at low level in MY1901 to reduce the toxicity of overexpression of Ffh. Then, the suppressor mutation (GAAG) was restored to wild-type SD sequence (GGAG) by site-directed mutagenesis, generating the strain MY1901FS. (D) Growth curves and growth rates of four strains: MG1655 and MY1901carrying the empty vector (EV) pTrc99K, MY1901F, and MY1901FS. Strains MG1655 and MY1901 carrying the empty vector pTrc99K were used as control. Solid curves are the mean of three independent measurements, and error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean value. Growth rates were figured out from the logarithmic phase. All growth rates shown represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Statistical significance compared to wild-type strain using Student’s t-test is indicated as follows: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.