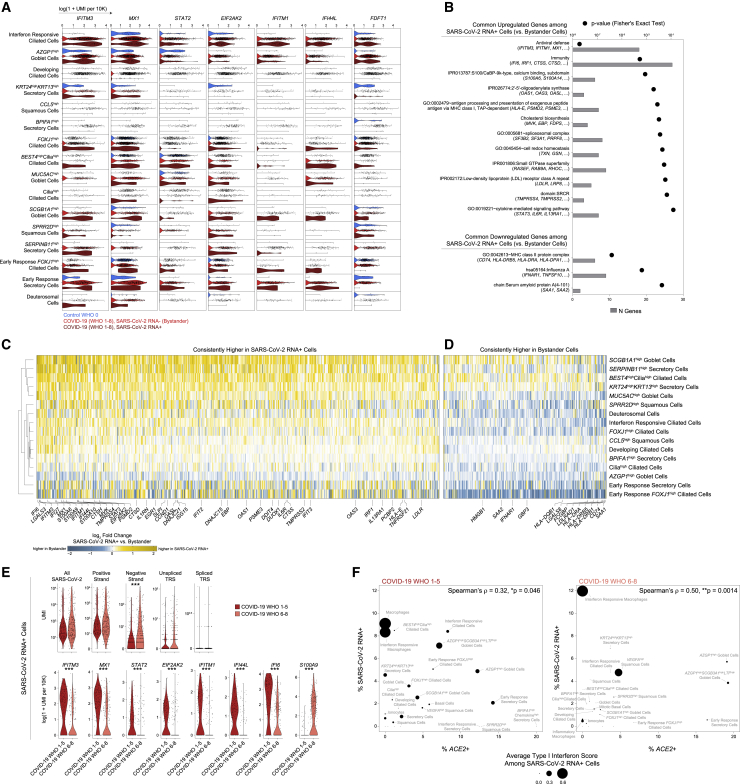
Figure 6.
Intrinsic and bystander responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection
(A) Violin plots of selected genes upregulated in SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells in at least three individual cell type comparisons. Blue, control participants; red, bystander cells from COVID-19 participants; dark red, SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells.
(B) Enriched gene ontologies among genes consistently up- or downregulated among SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells across cell types.
(C and D) Heatmap of genes consistently higher in SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells (C) and higher in bystander cells (D) across multiple cell types. Colors represent log fold changes between SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells and bystander cells. Yellow, upregulated among SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells; blue, bystander cells.
(E) Top: Violin plots of SARS-CoV-2 aligning reads among SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells. Statistical significance by Wilcoxon rank sum test. Bottom: select differentially expressed genes between SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells from participants with mild or moderate COVID-19 (red) versus severe COVID-19 (pink). Statistical significance by likelihood ratio test assuming an underlying negative binomial distribution. ∗∗∗ FDR-corrected p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05.
(F) Percent ACE2+ cells versus percent SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells by detailed cell type. Left: cells from participants with mild or moderate COVID-19. Right: cells from participants with severe COVID-19. Point size reflects average type I interferon-specific module score among SARS-CoV-2 RNA+ cells.