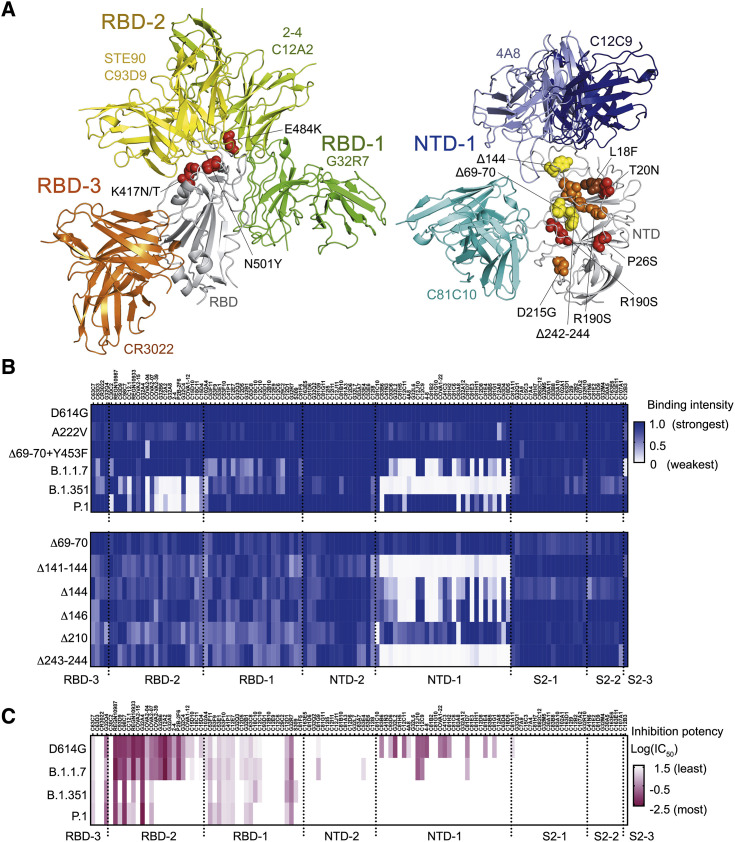
Figure 6.
Influence of mutations found in variants of concern on binding and neutralization by human mAbs
(A) Positions of mutations in amino acid sequences of B.1.1.7, B.1.351 and P.1. Left panel: RBD (gray backbone cartoon) and Fvs representing each of the three RBD clusters (green, yellow, and orange backbone cartoons for RBD-1, -2, and -3, respectively). Red spheres show side chains at positions of RBD mutations N501Y (found in all three variants of concern), E484K, and K417N/T (found in B.1.351 and P.1). Right panel: NTD (gray backbone cartoon) and Fvs representing the NTD-1 cluster (blue backbone cartoon) and the C81C10 non-neutralizing antibody (cyan backbone cartoon). Spheres show side chains at positions of mutations in B.1.1.7 (yellow), B.1.351 (orange), and P.1 (red). One NTD substitution, L18F (brown), is in both B.1.351 and P.1. Although Δ242-244 is a deletion within a β strand, its effect will be to reconfigure the 248–260 loop (orange asterisk), as residues 245–247 will shift into the positions of the deleted residues in the strand. See also Figure S6.
(B) Heatmap showing binding of 119 mAbs to Nextstrain cluster 20A.EU1 (A222V), Danish mink variant (Δ69-70 and Y453F), B.1.1.7 (Δ69-70, Δ144, N501Y, A570D, P681H, T716I, S982A, and D1118H), B.1.351 (L18F, D80A, D215G, Δ242-244, K417N, E484K, N501Y, and A701V), and P.1 (L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, H655Y, T1027I, and D1176F) (top), and NTD deletion variants (bottom). Variants include D614G. Relative binding intensities of the tested mAbs for each variant are shown in shades of blue.
(C) Heatmap showing neutralization potency of 119 mAbs to D614G, B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1. Log10 transformed IC50 shown in shades of dark red. IC50, μg/mL.
See also Figure S6.