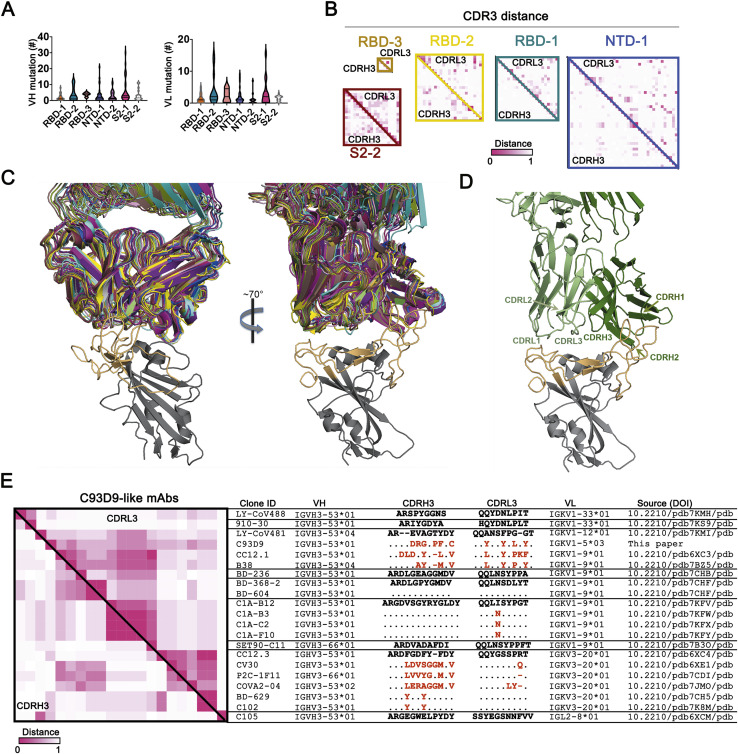
Figure S5.
Diversity of antibody sequences and convergent C93D9 class of antibodies, related to Figure 5
(A) V(D)J and VJ mutation levels in each of the 7 principal competition groups. Mutations in VH and VL (excluding CDR3) counted by IgBLAST. (B) Maps of pairwise distances of CDRH3 (lower left triangle) and CDRL3 (upper right triangle) for the RBD-1, RBD-2, RBD-3, NTD-1 and S2-2 cluster antibodies related to Figure 5B. (C) Two views of 20 Fab structures, listed in (E), bound with SARS-CoV-2 RBD. Structures all superposed on the RBD; heavy-and light-chains of each Fab in a distinct color. The figure includes only the RBD from 6YZ5 (not one of the 20), with the RBM in light orange and the rest of the chain in gray. (D) View as in the right-hand panel in (C), but showing only the Fab from 7B3O (the closest in sequence to C93D9), with CDRs labeled. The most intimate contacts with RBM residues are from CDRH1, CDRH2 and CDRL1, many with residues constrained in potential variability by ACE2 interaction. (E) Maps of pairwise distances of CDRH3 (lower left triangle) and CDRL3 (upper right triangle) for the 21 C93D9 class antibodies in (C) and (D). Pairwise distances analyzed by MEGA X. Intensity of color shows the distance, from 0 (identical) to 1 (no identity). The VH and VL genes encoding the antibodies are shown in the indicated groups. Differences in CDR3s from the reference sequences (bold) are in red; dashes indicate missing amino acids; dots represent identical amino acids. IGHV3-66 and IGHV3-53 are very similar VH gene segments, differing by only one encoded amino-acid residue.