FIGURE 1.
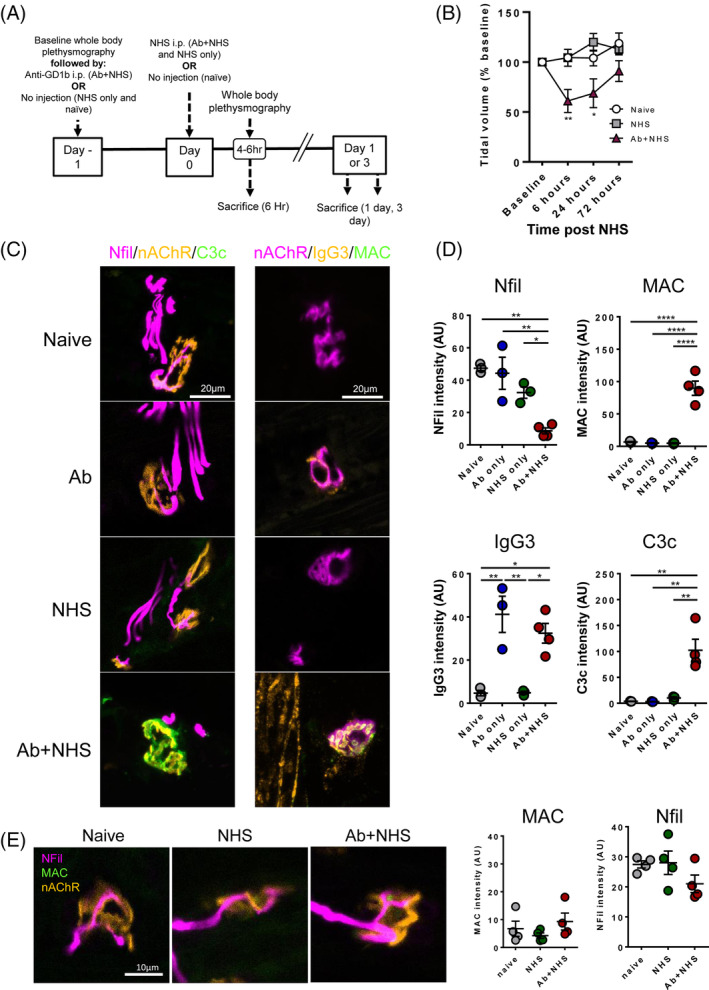
Lowered doses of anti‐ganglioside antibody (AGAb) and complement allows sufficient injury to distal nerve while allowing survival and recovery of injured mice. A, Protocol of model showing treatments given to mouse groups. B, Whole‐body plethysmography (n = 4/group) of AB + normal human serum (NHS)‐treated mice showed measurable reduction in tidal volume within 6 hours of NHS treatment vs naïve mice. After 24 hours, tidal volume was still affected but by 72 hours, it had returned to levels comparable with naive mice. NHS‐treated mice showed no difference vs naïve mice. C, Illustrative images show lack of C3c and MAC at neuromuscular junction (NMJs) of control mice while in Ab + NHS‐treated mice C3c and MAC can be seen overlying the NMJ. This corresponds with a loss of neurofilament (NFil) staining at the NMJ. D, Quantification of intensity of immunofluorescent staining for NFil, MAC, IgG3, and C3c overlying BTx signal. Ab + NHS‐treated mice showed significantly increased the presence of complement products C3c and MAC and significantly reduced NFil intensity. IgG3 was comparable between Ab only and Ab + NHS‐treated mice. E, At 3 days post‐NHS, mice from all groups had comparable levels of MAC and NFil. * = P < .05, ** = P < .01, *** = P < .001, **** = P < .0001, one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test
