Fig. 2. |. Detailed interfaces in the NLRP1-DPP9 ternary complex and inhibition by the DPP9 inhibitor VbP.
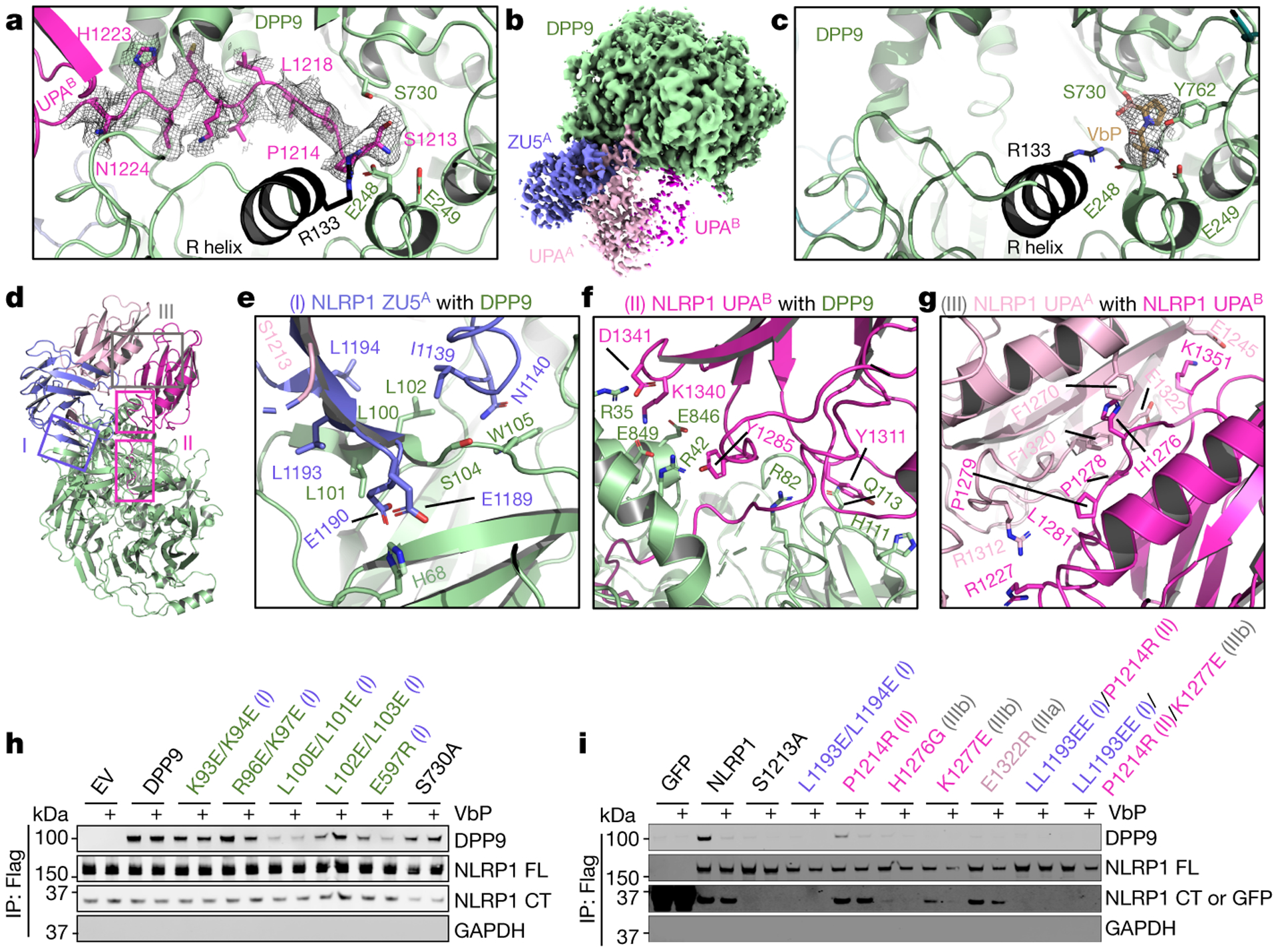
a, Insertion of the N-terminal peptide of UPAB into the DPP9 active site. b, Cryo-EM map of the NLRP1-DPP9 complex in the presence of VbP. VbP binding reduces UPAB occupancy. c, Displacement of the UPAB N-terminal peptide from the DPP9 active site by VbP. d, Overview of three interfaces important for NLRP1-DPP9 association. Regions blocked in rectangles are shown in detail in (a) and (e-g). e-g, Zoom-ins of each NLRP1-DPP9 binding interface. h, FLAG co-immunoprecipitation using FLAG-tagged WT NLRP1 and the indicated His-tagged DPP9 constructs expressed in DPP8/9 DKO 293T cells. EV: empty vector. i, FLAG co-immunoprecipitation using FLAG-tagged NLRP1 expressed in HEK293T cells. FLAG-tagged GFP was used as a negative control. The Roman numerals in parentheses (h-i) represent the three interfaces in the NLRP1-DPP9 ternary complex. Each immunoblot is representative of > 2 independent experiments.
