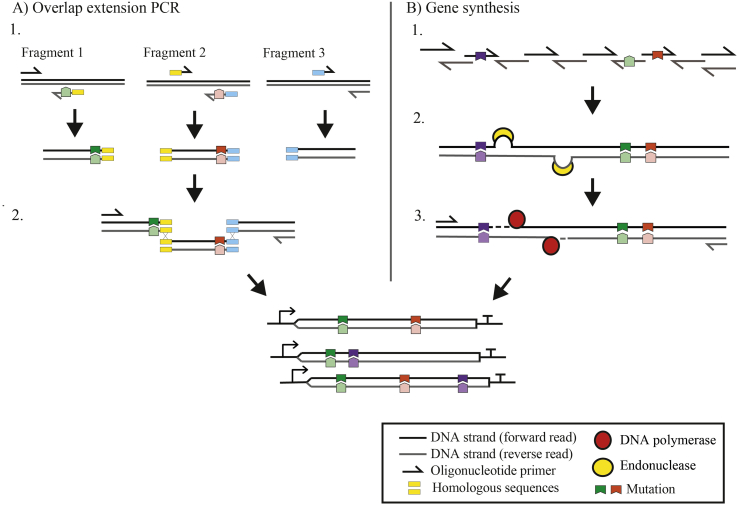
Fig. 5.
Synthesis of combinatorial libraries using PCR-based methods. A) OE-PCR (1.) first amplifies the gene fragments using oligonucleotide primers that encode both mutations and homologous terminal sequences. 2. Joining of the fragments is controlled by homologous sequences priming overlap extension during the second PCR. B) Gene synthesis assembles the desired sequence by (1.) OE-PCR, encoding mutations on the overlapping oligonucleotide primers. 2. Following an error correction step using an endonuclease the (3.) full length library sequence is assembled in a second PCR step.