Fig. 2.
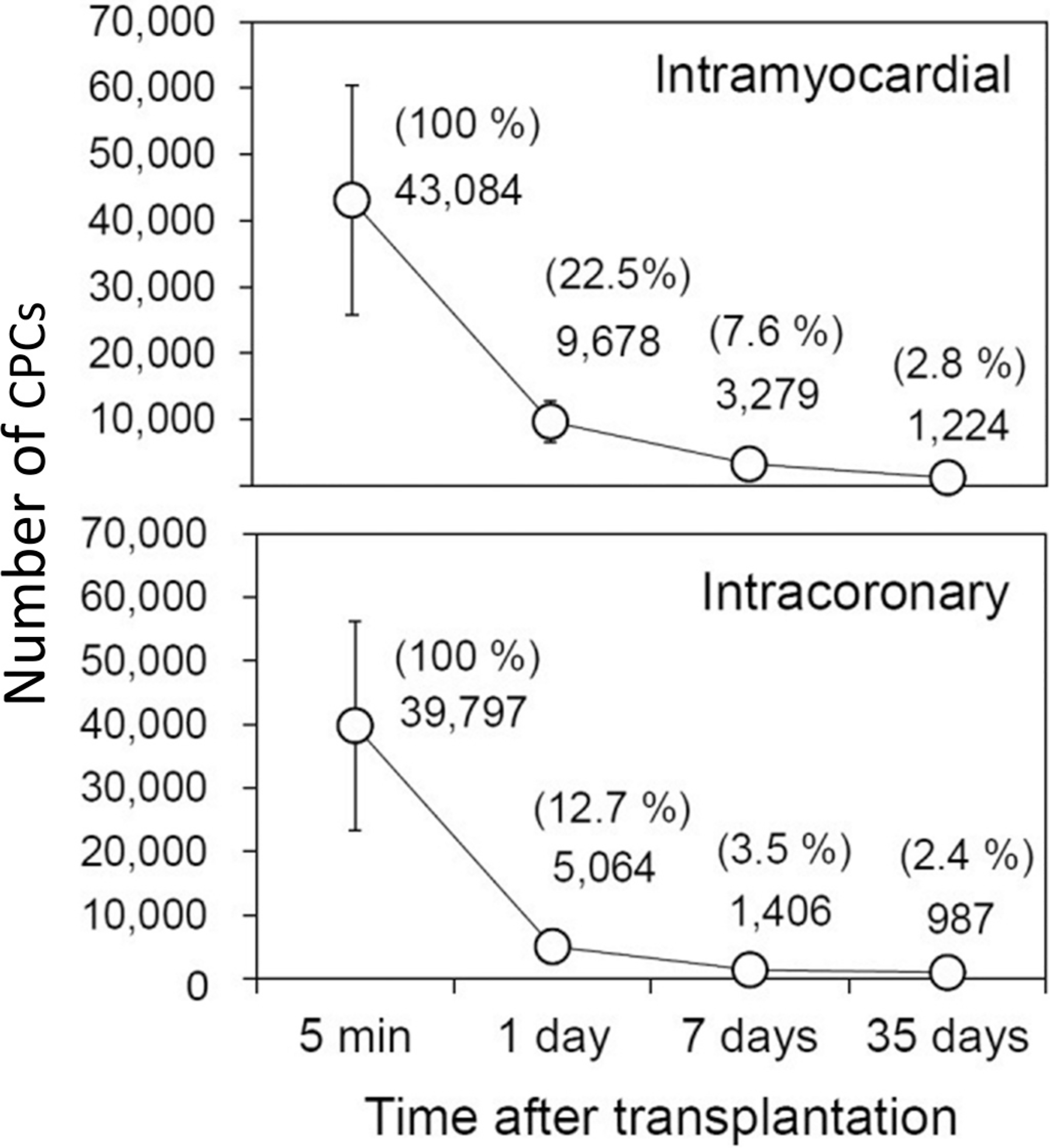
Comparison of CPC retention and engraftment after intramyocardial and intracoronary delivery in mice with acute MI. Female mice with acute MI were given 105 male c-kit+ CPCs by the intramyocardial (upper panel) or intracoronary (present study; lower panel) route. The CPC content in the heart was measured with a highly sensitive PCR-based method that can precisely quantify the number of male transplanted cells in female recipients by assessing a male gene. The absolute numbers of CPCs detected in the entire heart at indicated time points are shown. The number of cells found at each time point, expressed as a percentage of the cells found at 5 min after delivery, is shown in parentheses. Note that the number of CPCs retained in the heart drops precipitously after transplantation irrespective of the route used to inject them; only a miniscule fraction (<3%) of transplanted CPCs could be found in the heart 35 days after transplantation (<1500 cells per heart), yet LV function was improved at this time point. Data are means ± SEM. Reproduced from Hong et al. (2014).
