Fig. 5.
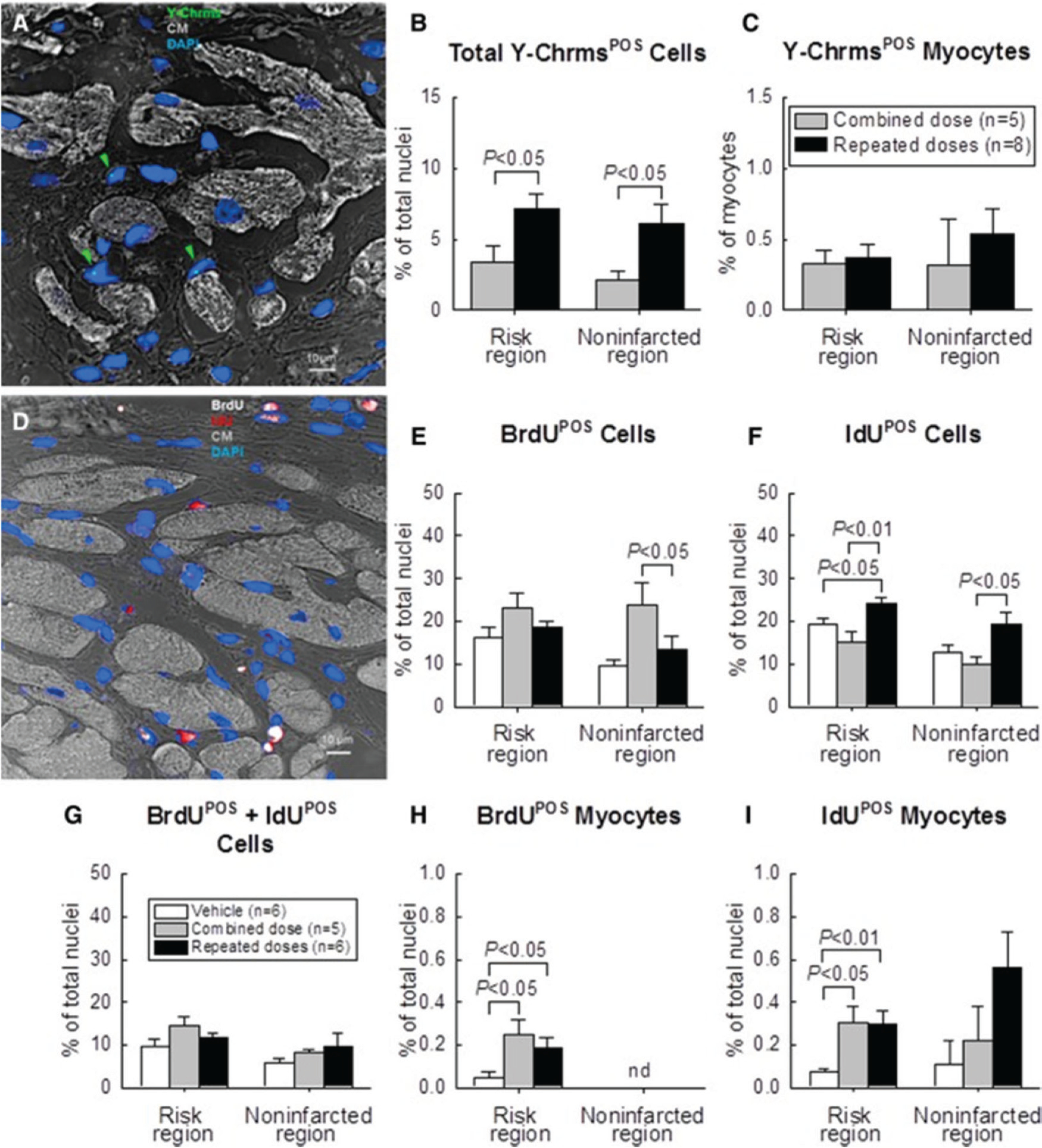
Detection of CPC retention and engraftment with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for detection of Y-chromosomes (Y-Chrms) after multiple CPC administrations in rats with chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy. Male c-kit CPCs were injected into female rats with old MI 30 days after MI; rats received either one combined dose or three CPC injections at 35-day intervals. Rats were given BrdU or IdU after CPC transplantation. (A) Representative confocal microscopic image acquired from the infarcted region. Green arrowheads indicate Y-chromosome fluorescent signals (green/cyan) in nuclei. Nuclei are stained with DAPI in blue. Cardiomyocyte (CM) morphology was examined with a confocal transmitted light channel’s detector (ChD) in which the pseudocolor selected for myocardial background in the ChD channel was gray white. (B) Quantitative analysis of the number of total Y-chromosomePOS cells and (C) Y-chromosomePOS matured myocytes at 105 days after CPC transplantation. The risk region comprises both the border zones and the infarcted region. (D) Representative confocal microscopic image acquired from the border zone. BrdU (given in the first 35 days after start of treatment) is shown in white, and IdU (given on days 70 to 105 after start of treatment) is shown in red. Nuclei are stained with DAPI. Cardiomyocyte (CM) morphology was examined with the confocal transmitted light ChD; the pseudocolor selected for myocardial background in the ChD channel was gray white. (E–G) Quantitative analysis of the number of BrdUPOS, IdUPOS, and BrdUPOS/IdUPOS nonmyocytes at 105 days after start of CPC administration. (H–J) Quantitative analysis of the number of BrdUPOS and IdUPOS myocytes at 105 days after start of CPC administration. (“Myocytes” were defined as α-sarcomeric actin positive cells, but these cells were small and did not resemble mature myocytes.) The risk region comprises both the border zones and the infarcted region. Note that the number of newly formed (i.e., BrdUPOS and (or) IdUPOS) cardiomyocytes (regardless of their source, exogenous or endogenous) was negligible (<1% of nuclei); that is, transplantation of CPCs did not promote significant formation of new cardiomyocytes from either exogenous or endogenous (resident) cells, even after multiple CPC doses. Data are means ± SEM. BrdU, 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; IdU, 5-iodo-2′-deoxyuridine. Reproduced from Tang et al. (2018).
