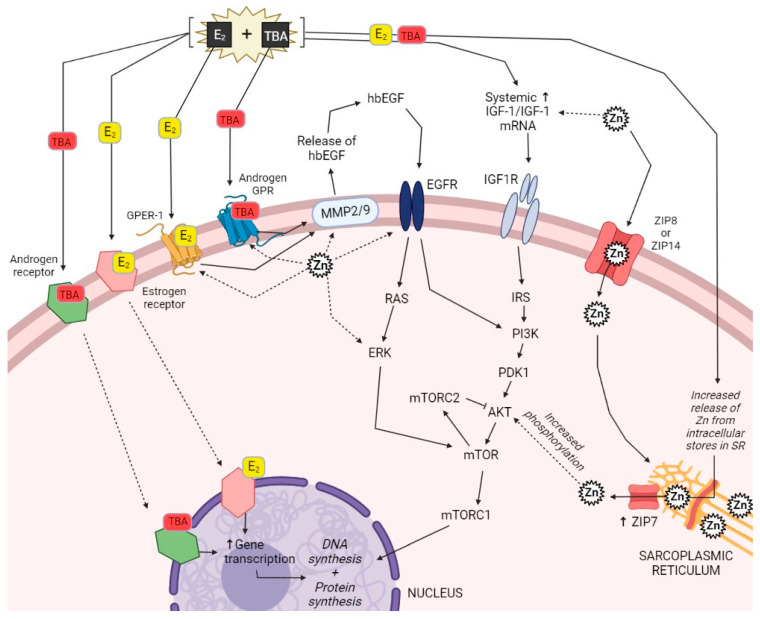
Figure 1.
Proposed physiological pathway interactions of combination E2 + TBA steroidal implants and Zn in skeletal muscle cells as discussed in this review. Specific focus is placed on the genomic and non-genomic steroid hormone pathways, protein and DNA synthesis pathway, and the corresponding points at which evidence suggests Zn interacts with these pathways. Definitions: AKT (Protein kinase B), Androgen GPR (Androgen specific G protein-coupled receptor), E2 (Estradiol), EGFR (Epidermal growth factor receptor), ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinase), GPER-1 (G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1), hbEGF (Heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor), IGF-1 (Insulin-like growth factor 1), IGF1R (Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor), IRS (Insulin receptor substrate), MMP2/9 (Matrix metalloproteinase 2/9), mTOR (Mammalian target of rapamycin), mTORC1 (Mammalian target of rapamycin 1), mTORC2 (Mammalian target of rapamycin 2), PDK1 (Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1), PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinases), RAS (Ras family of related GTPase proteins), SR (Sarcoplasmic reticulum), TBA (Trenbolone acetate), ZIP7 (Zinc transporter SLC39a7), ZIP8 (Zinc transporter SLC39a8), ZIP14 (Zinc transport SLC39a14).