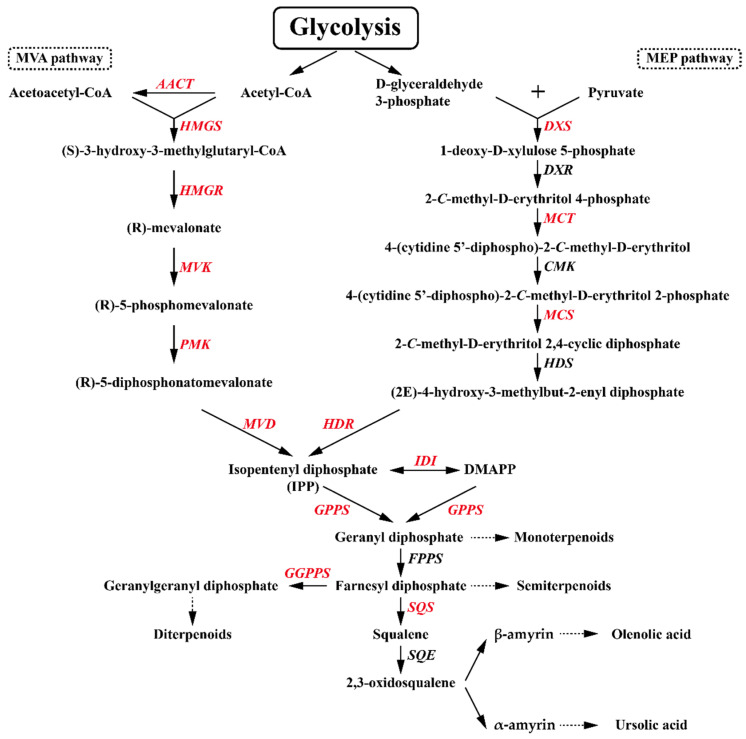
Figure 2.
The proposed pathway for the biosynthesis of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid. The terpenoid biosynthetic genes identified in this study are indicated in red: MVA, mevalonic acid; MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; DMAPP, isomer dimethylallyl diphosphate; AACT, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; HMGS, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase; HMGR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; MVK, mevalonate kinase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; MVD, mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate decarboxylase; DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase; MCT, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase; CMK, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; MCS, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl-diphosphate synthase; HDR, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase; IDI, isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase; GPPS, geranyl diphosphate synthase; GGPPS, geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase; FPPS, farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase; SQS, squalene synthase; and SQE, squalene epoxidase.