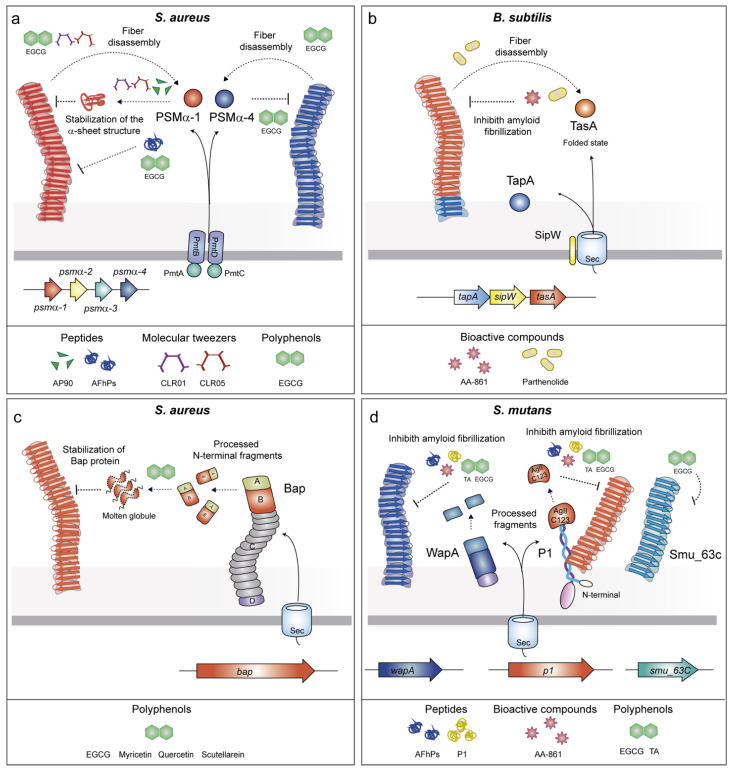
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the genes involved in the assembly of facultative amyloids, the drugs targeting such structures and their mechanism of action. (a) Drugs targeting S. aureus PSMs act by several mechanisms that involve the stabilization of PSM α-sheet structure and fiber disassembly. (b) B. subtilis TapA polymerization is inhibited by AA-861 and parthenolide. (c) The flavonoids quercetin, myricetin, and scutellarein inhibit polymerization of the Bap amyloid aggregates by stabilization of the Bap protein. (d) Polymerization of the amyloids S. mutants WapA and AgII/C123 is inhibited by AA-861, Tannic acid (TA), and EGCG and indirectly by the AFhPs and P1 peptides. SMU_63c amyloids are inhibited by EGCG.