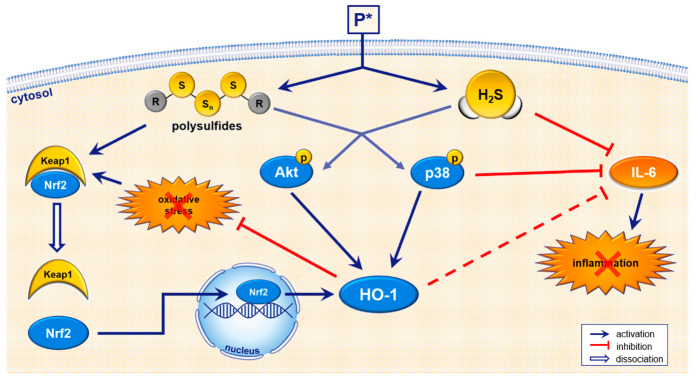
Figure 10.
Schematic summary of P*-mediated biological effects. In aqueous buffers, P* generates a metastable persulfide and a mixture of polysulfides as end-products [38]. Upon entry into the cell, P* also releases H2S in the presence of thiols such as cysteine or glutathione. Sulfhydration of proteins is mainly carried out by polysulfides, leading to the activation of Nrf2/HO-1 dependent antioxidant pathways. P* also induces HO-1 via the regulation of Akt and p38 MAPK. Apart from antioxidant effects, P* also shows anti-inflammatory properties such as the inhibition of IL-6 for which H2S and p38 MAPK seem to be responsible.