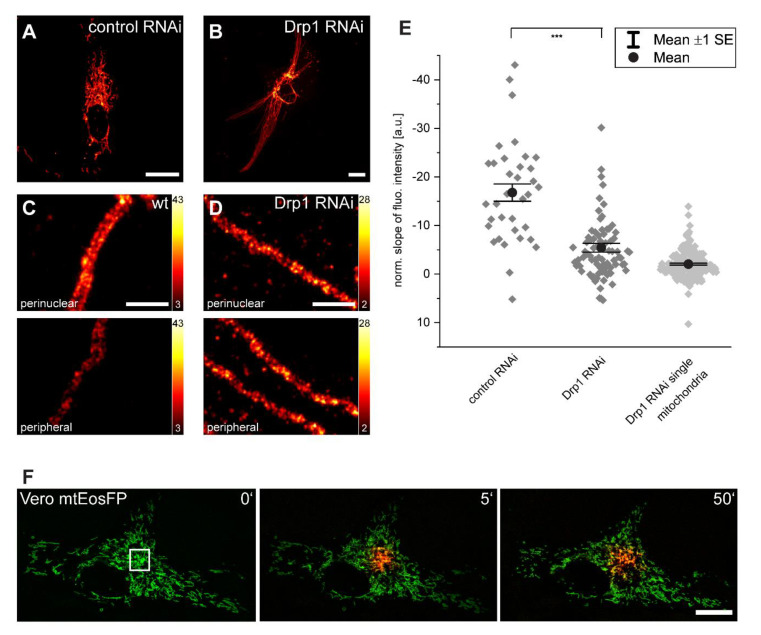
Figure 4.
Inhibition of mitochondrial fission reduces inner-cellular Tom20 protein abundance gradients. (A,B) RNAi-mediated knockdown of Drp1 leads to the elongation of mitochondria and the hyperfusion of the mitochondrial network. (C,D) Representative STED images of perinuclear and peripheral mitochondria in control (C) and Drp1-knockdown (D) cells labeled with a Tom20 antibody. Normalized slopes of the fluorescence intensity gradients of control and of Drp1-knockdown cells, and of single mitochondria in Drp1-knockdown cells decorated with antiserum against Tom20. (E) For the analysis, overlapping mitochondria were excluded. *** p = 0.001 (paired t test analysis). Each dark grey rhomb (control RNAi and Drp1 RNAi) represents one cell; each light grey rhomb (Drp1 RNAi single mitochondria) represents one mitochondrion. Black dot: mean. Error bars: standard error of the mean. Live-cell confocal imaging of Vero cells expressing mitochondrial matrix targeted mtEosFP. (F) At t = 0 min in the indicated area, the green fluorescent mtEosFP was photoconverted into its red fluorescent form. Subsequently, the spreading of the photoconverted mtEosFP was recorded. Scale bars: 1 µm (C,D), 20 µm (A,B,F).