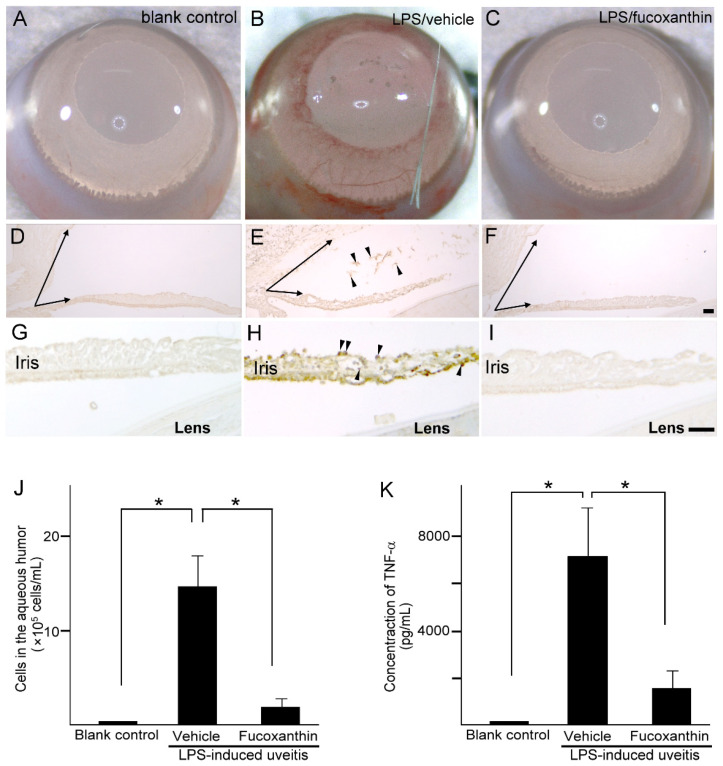
Figure 4.
Effects of fucoxanthin on iris hyperemia, inflammatory cells, and TNF-α protein concentrations. Compared to the blank control group (A), iris hyperemia was observed in the LPS/vehicle group (B). These signs were alleviated in the LPS/10 mg/kg BW of fucoxanthin group (C). Moreover, the abundance of inflammatory cells was evaluated by immunohistochemical analysis of MPO-positive leukocytes in the blank control (D,G), LPS/vehicle (E,H), and LPS/fucoxanthin (F,I) groups. A narrowed anterior chamber angle and number of MPO-positive leukocytes (arrowheads) in the aqueous humor (E) and iris (H) were found in the LPS/vehicle group compared to the control group (D,G). In contrast, a relatively wider anterior chamber angle and a decreased number of MPO-positive leukocytes were observed in the aqueous humor (F) and iris (I) of the LPS/fucoxanthin group compared to that of the LPS/vehicle group. In addition, the aqueous humor was collected to count the number of cells (J) and to measure the expression levels of the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α (K). The cell count and TNF-α expression levels were increased in the LPS/vehicle group, whereas the number of inflammatory cells and the TNF-α levels in the fucoxanthin-treated groups were significantly decreased. The results are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5). * p < 0.05: Compared to the LPS/vehicle group (Student’s t-test). Scale bars: 100 μm.