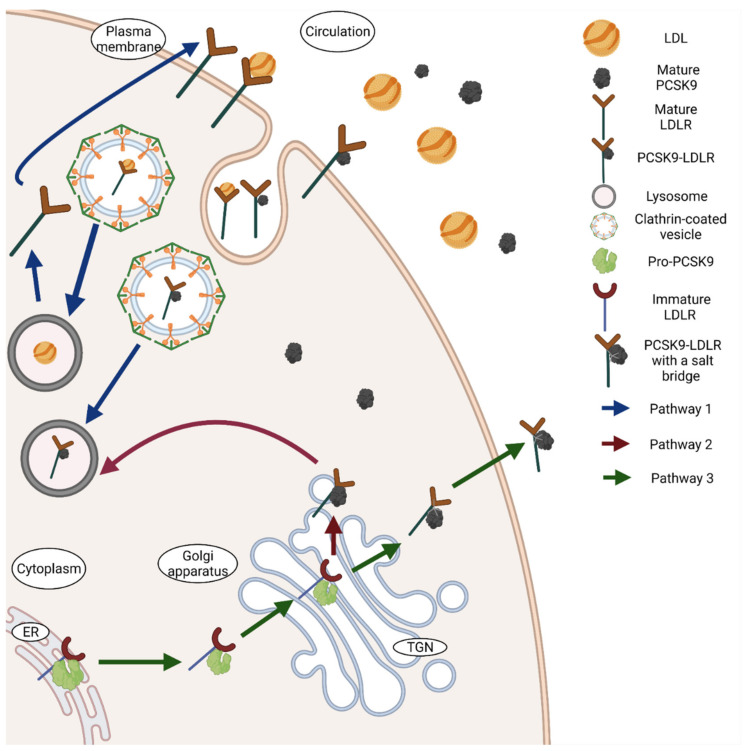
Figure 2.
Interactions between PCSK9 and LDLR. PCSK9 interacts with LDLR through three different approaches. Pathway 1 is represented in the figure with blue arrows, while pathway 2 with red arrows and pathway 3 with green arrows. Typically, LDLR on the surface binds to the circulating LDL and transports the cholesterol particle through clathrin coated pits for degradation by lysosomes. The receptor then gets recycled back to the surface. In the presence of PCSK9, a bond between the epidermal growth factor-A (EGF-A) domain of LDLR and the catalytic domain of PCSK9 is formed. PCSK9 transports LDLR via clathrin-coated vesicles to lysosomes for degradation. In this process, PCSK9 gets degraded as well (pathway 1). Intracellularly, PCSK9 binds in the same manner with LDLR in the Trans-Golgi network (TGN) and directs the compound again towards lysosomes (pathway 2). Lastly, Pro-PCSK9 also binds to LDLR in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and transports the complex to Golgi apparatus, where both PCSK9 and LDLR undergo maturation. The matured PCSK9 binds to LDLR with an additional salt bridge that is released from the cells into circulation (pathway 3). The figure was created with Biorender.com (accessed on 19 May 2021).