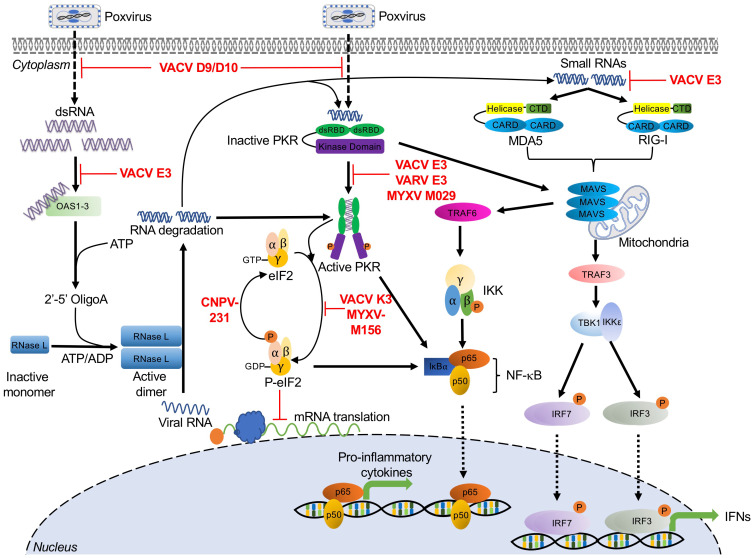
Figure 1.
dsRNA sensor-mediated signaling pathways and poxvirus antagonists. The figure presents host sensors (black text) involved in recognizing dsRNA species from poxviral infections, and the elicited signaling cascades by these sensors, which are indicated by black arrows. Poxvirus-encoded immunomodulatory proteins that inhibit activation of these host pathways are indicated in red text and their effects on pathways are indicated by red lines. See main text for corresponding details and the underlying molecular mechanisms. Abbreviations used in this figure include ADP: adenosine diphosphate; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; CARD: caspase activation and recruitment domains; CNPV: canarypox virus; CTD: carboxy-terminal domain; dsRBD: dsRNA binding domain; dsRNA: double-stranded RNA; eIF2: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2; GDP: guanosine diphosphate; GTP: guanosine-5′-triphosphate; IKKα: IκBα kinase α; IKKβ: IκBα kinase β; IKKε: IκBα kinase ε; IKKγ: IκBα kinase γ; IL-6: interleukin-6; IRF3/7: interferon regulatory factor 3/7; IκBα: inhibitor κBα; MAVS: mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MDA5: melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; MYXV: myxoma virus; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; OAS: 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetases; p65/p50: NF-κB heterodimer p50/p65 subunit; PKR: protein kinase R; RIG-I: retinoic acid-inducible gene I; RNase L: ribonuclease L; TBK1: TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator (TANK)-binding kinase 1; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TRAF3/6: tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3/6; VACV: vaccinia virus; VARV: variola virus.