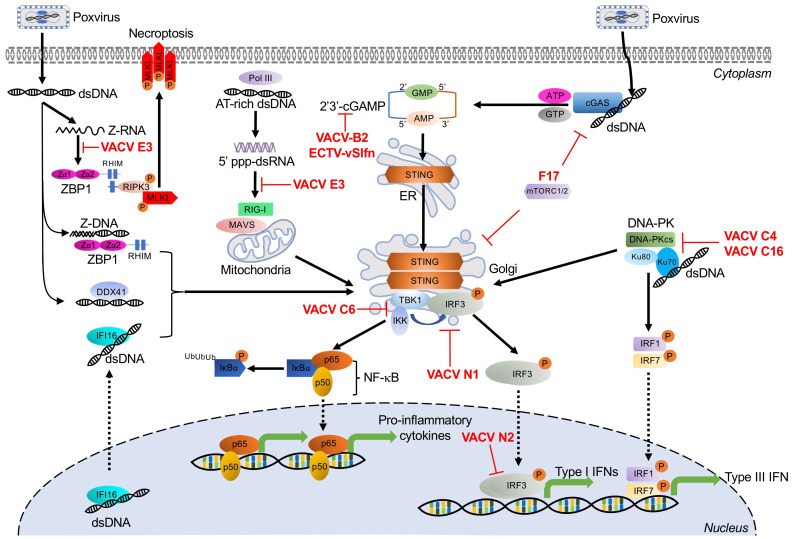
Figure 2.
Cytosolic DNA sensor-mediated signaling pathways and poxvirus antagonists. DNA sensors are denoted in black text and the transduction of their triggered signaling cascades are indicated by black arrows. The diverse poxviral inhibitors of these cytosolic DNA sensors are indicated in red. See main text for corresponding details and the underlying molecular mechanisms. Abbreviations used in this figure include ADP: adenosine diphosphate; AMP: adenosine monophosphate; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; cGAS: cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; DDX41: Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD) box polypeptide 41; DNA-PK: DNA-dependent protein kinase; DNA-PKcs: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit; dsDNA: double-stranded DNA; ECTV: ectromelia virus; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; GMP: guanosine monophosphate; IFI16: interferon-γ inducible protein 16; IL-6: interleukin-6; IRF1/3/7: interferon regulatory factor 1/3/7; IκBα: inhibitor κBα; MAVS: mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MLKL: mixed lineage kinase-like; mTORC1/2: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1/2; MVA: modified vaccinia virus Ankara; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; p50/p65: NF-κB heterodimer p50/p65 subunit; RHIM: RIP homotypic interaction motif; RIG-I: retinoic acid-inducible gene I; RIPK: receptor interacting protein kinase; RNA pol III: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase III; STING: stimulator of interferon genes; TBK1: TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator (TANK)-binding kinase 1; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TRAF: tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor; VACV: vaccinia virus; vSlfn: viral Schlafen; ZBP1: Z-nucleic acid-binding protein 1; Zα: Z-nucleic acid binding domain; 2′3′ cGAMP: 2′3′ cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate; 5′ppp-dsRNA: 5′ triphosphate double-stranded RNA.