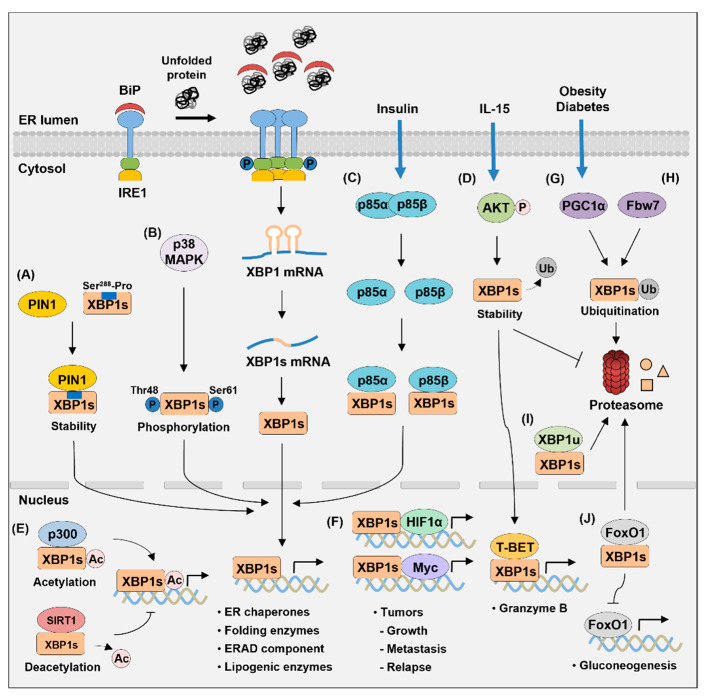
Figure 4.
Proteins interacting with XBP1s. XBP1s interacts with a variety of other proteins, and these molecular mechanisms are important for regulating the protein stability and transcriptional activity of XBP1s. (A) XBP1s interacts with PIN1 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, and this interaction increases the stability of XBP1s. XBP1s interacts with the WW domain of PIN1 via the Ser288-Pro motif of XBP1s. (B) The p38 MAPK directly phosphorylates the Thr48 and Ser61 residues of XBP1s, thereby enhancing the nuclear translocation of XBP1s [134]. (C) Insulin induces the interaction of XBP1s with p85α and p85β, the regulatory subunits of PI3K, leading to increased nuclear translocation of XBP1s. (D) IL-15 induces the phosphorylation of AKT, which increases the stability of XBP1s by inhibiting ubiquitination. XBP1s interacts with T-BET to bind to the proximal region of the granzyme B promoter. (E) XBP1s is regulated at the post-translational level via acetylation and deacetylation, mediated by its interaction with p300 and SIRT1, respectively. (F) XBP1s forms a transcriptional complex with HIF1α, which increases the tumorigenicity and progression of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). XBP1s also forms a complex with MYC, enhancing the transcriptional activity of XBP1s in tumors. (G) PGC1α reduces the XBP1s stability, which negatively affects the activity and protein level of XBP1s. PGC1α and XBP1s interact with each other in their activation domains to promote the protein degradation of XBP1s via ubiquitination. (H) Fbw7 interacts with XBP1s in a phosphorylation-dependent manner to promote the ubiquitination and degradation of XBP1s. (I) XBP1u functions as a negative feedback regulator of XBP1s via direct interaction. The complex of XBP1u and XBP1s is rapidly degraded by the proteasomes due to the degradation domain contained in XBP1u. (J) XBP1s binds directly to the FoxO1 and facilitates the degradation of FoxO1 via the 26S proteasome pathway. FoxO1 is a transcription factor that regulates gluconeogenesis by increasing the expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose 6 phosphatase.