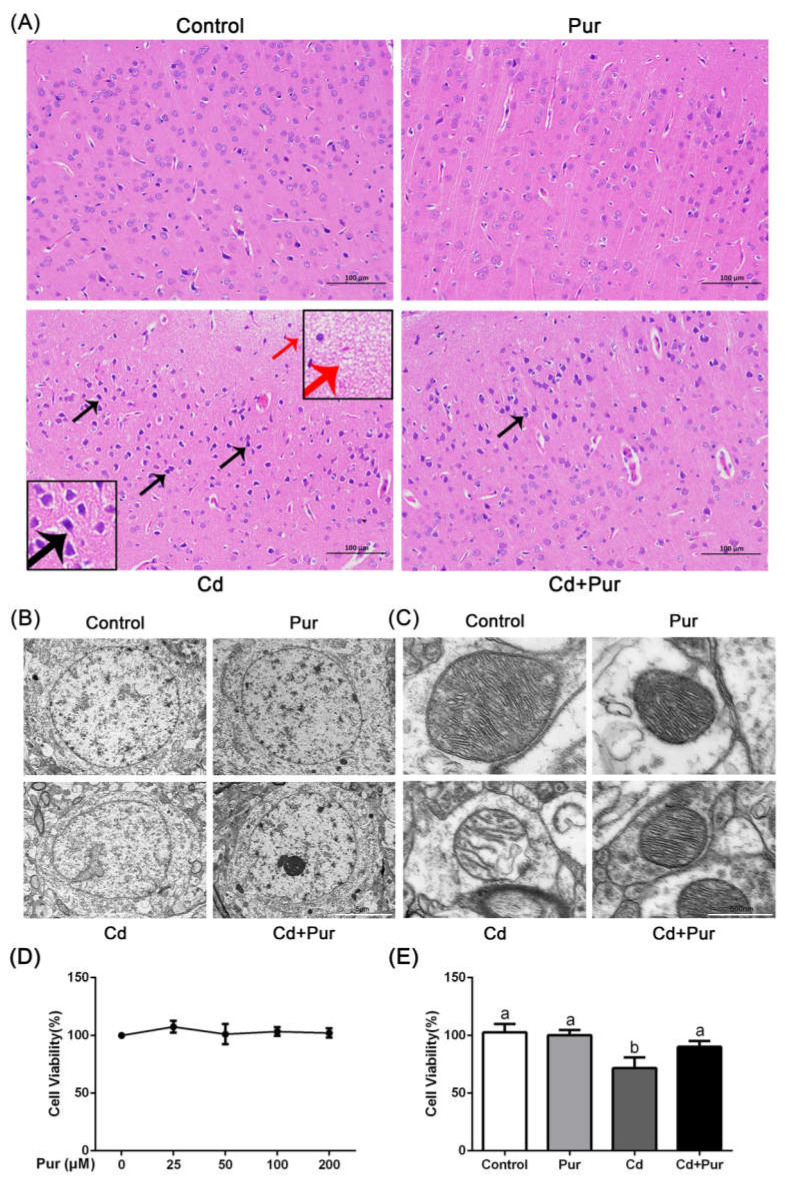
Figure 1.
Pur alleviates Cd-induced neuronal injury. Rats were treated with Cd (50 mg/L) and/or Pur (200 mg/kg) for 90 days. (A) H&E staining of the rat cerebral cortices of each group. A period of 90 days of Cd exposure induced the formation of microscopic voids in the cortex (red arrows), neuronal deep staining, unclear boundaries between the cytoplasm and nuclei, as well as gaps around the neurons (black arrows). Treatment with Pur attenuated Cd-induced neuronal injury in the rat cerebral cortices. Scale bars: 100 μm. Representative electron microscopy images show the (B) nuclei and (C) mitochondria in the rat cerebral cortices of each group. Scale bars: (B) 5 μm and (C) 500 nm. (D) Primary cortical neurons were treated with different concentrations of Pur (0 μM–200 μM) for 12 h. Cell viability was detected using a CCK-8 assay. (E) Primary cortical neurons were pretreated with 100 μM Pur for 1 h, followed by exposure to 10 μM Cd for 12 h, after which the cell viability was detected via a CCK-8 assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 4). The means labeled without a common letter (a, b) are significantly different, p < 0.05.