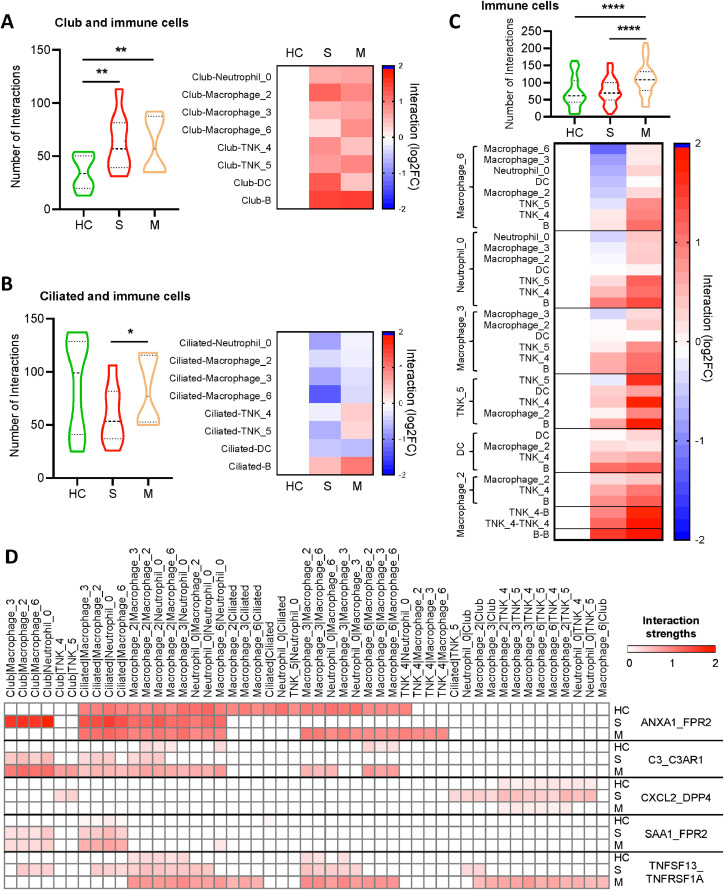
Fig. 3.
SARS-CoV-2 infection resulted in abnormal epithelial-immune cell interaction in lung. (A-C) We evaluated intercellular communications based on expression of ligand–receptor pairs among different cell types by CellPhoneDB. Club-immune cells (A), ciliated-immune cells (B), and immune-immune communications (C) in severe (S, n=6), recovered mild (M, n=3) COVID-19 patients, and healthy controls (HC, n=10) were shown. Only significant interactions were calculated, and the number of interactions was depicted in violin plot, or normalized against those of healthy controls in heatmap. (C) Heat map depicting different ligand–receptor interactions among different cell types. Interaction strengths are color coded. [One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey multiple comparisons (A-C)]. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; **** P < 0.0001.