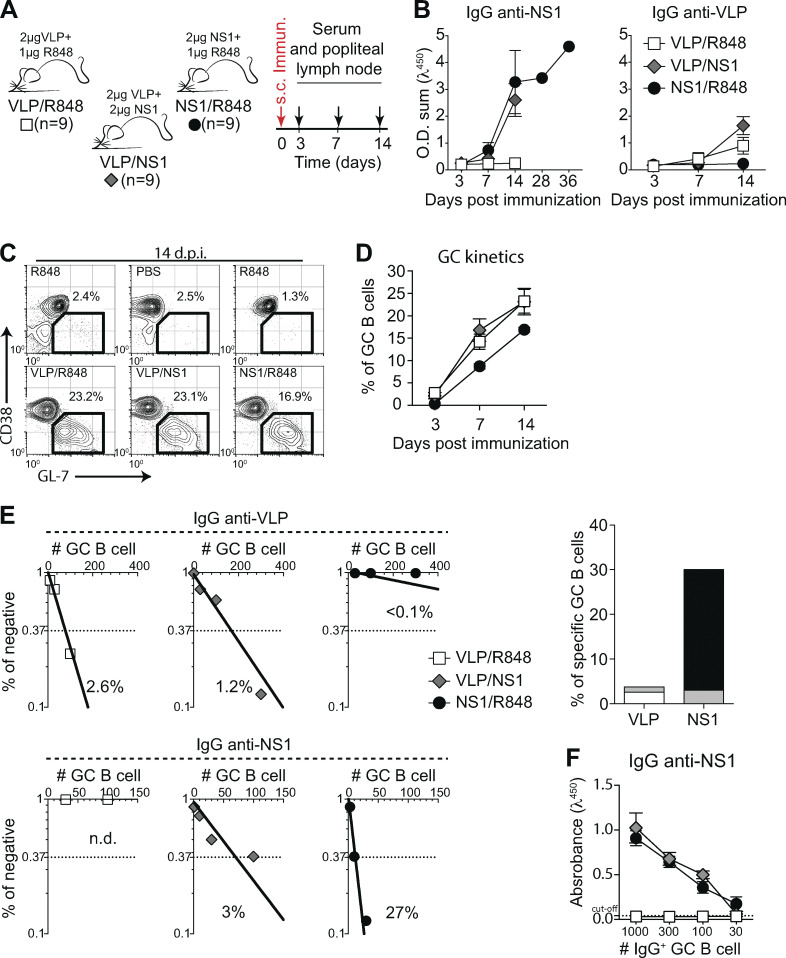
Figure 4.
Antigen specificity of B cells in GCs after immunization with ZIKV VLP and NS1. (A) Experimental design indicating the time points of serum samples and popliteal LNs collections after immunization with NS1 (2 μg/mouse), VLP (2 μg/mouse) or both (2 μg of NS1 and 2 μg of VLP/mouse). Immunizations were adjuvanted with R848 (1 μg/mouse). (B) Kinetics of serum levels of IgG binding to ZIKV NS1 recombinant protein or ZIKV VLP, measured by ELISA. O.D. sum is the sum of ODs of four serum dilutions (1:40, 1:120, 1:360, and 1:1,080). (C) Representative plots of GC B cells (CD38lo/− GL-7+ gated on B220+ CD138−) at day 14 after immunization. Mice were immunized on the left footpad. (D) Kinetics of frequency of GC B cells in left popliteal LNs after immunization. (E) GC B cells from popliteal LNs of immunized mice were sorted and cultured in decreasing numbers per well (300, 100, 30, and 10 cells per well). Supernatants were collected on day 7 and screened for IgG secretion by ELISA. Supernatants that revealed the presence of IgG were tested for antigen specificity by ELISA. Frequencies of IgG+ GC B cells that bound VLP (upper panel) or NS1 (lower panel) were calculated using Poisson distribution and are summarized on the right graph. n.d., not detected. Cell culture was performed on a monolayer of gamma-irradiated (20 Gy) NB21 feeder cells (Kuraoka et al., 2016; 3 × 103 cells/well) and LPS (30 µg/ml). (F) OD of IgG+ supernatants of different cell numbers/well binding to ZIKV NS1, measured by ELISA. Data are representative of two independent experiments with nine mice per group. Error bars represent SEM.