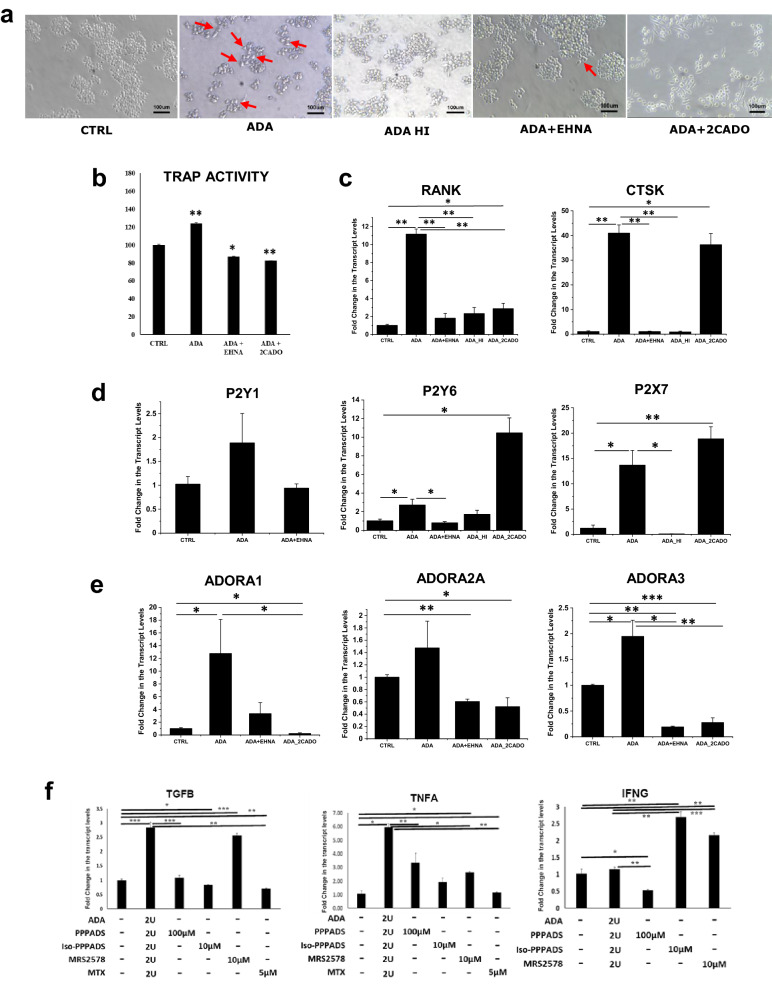
Figure 6.
ADA enhances adenosine signaling and purinergic receptor signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. (a) Osteoclast differentiation is reduced after exposure to EHNA (ADA blocker) and 2CADO (adenosine analog) in macrophages. (b) Reduced TRAP activity after the treatment with EHNA and 2CADO confirming the role of ADA in osteoclast differentiation. (c) Decreased expression of osteoclast markers CTSK and RANK in macrophages after exposure to EHNA and 2CADO. (d) Decreased expression of P2Y receptors after exposure to EHNA and 2CADO along with ADA shows involvement of P2Y receptors in osteoclast differentiation. (e) Enhanced Adenosine signaling with the exposure of ADA in macrophages leading to increased expression of adenosine receptors. (f) Decreased expression of inflammatory genes after exposure to P2 receptor antagonists in the presence of ADA (showing *representing a p value of ≤ 0.05, and **representing a p value of ≤ 0.005, ***representing a p value of ≤ 0.0005). All the plots were made using Origin 2020.