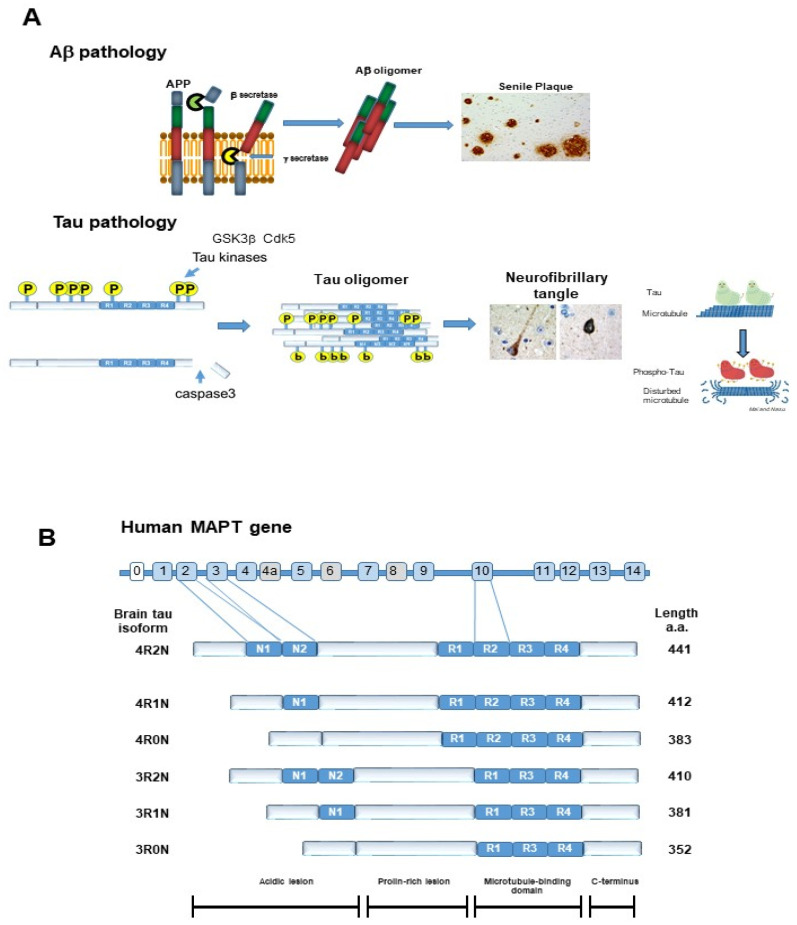
Figure 1.
Pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. (A) Amyloid β protein (Aβ) was generated by cleaving amyloid precursor protein (APP) with β secretase and γ secretase. Aβ forms oligomers and finally forms senile plaques. Once tau protein is hyper-phosphorylated by tau kinases, including GSK3β or cdk5, it detaches from the microtubule and forms aggregates, called tau oligomers. C terminal-truncated tau by caspase3 and N-terminal truncation accelerates tau aggregation. Tau oligomers are neurotoxic and further aggregation leads to neurofibrillary tangles (NFT). (B) Tau isoforms and phosphorylation epitopes. There are 6 tau isoforms according to the number of N terminal insertions and repeats of the microtubule binding domain: 4 repeat 2 N (4R2N), 4 repeat 1N (4R1N), 4 repeat 0N (4R0N), 3 repeat 2N (3R2N), 3 repeat 1N (3R1N), and 3 repeat 0N (3R0N).