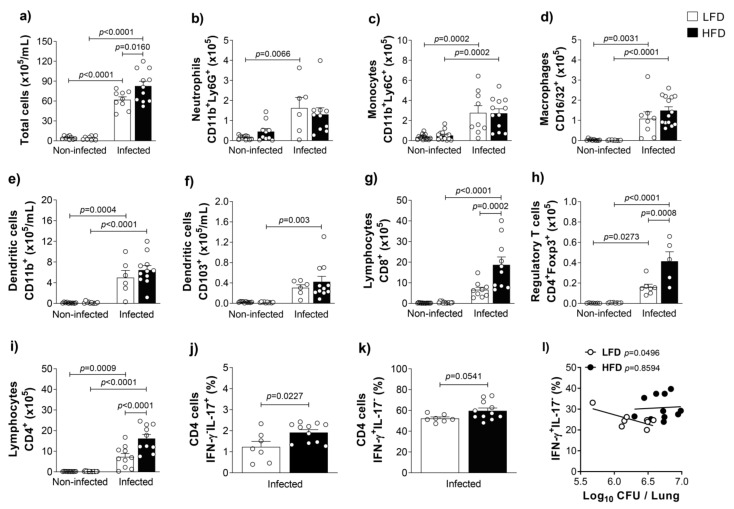
Figure 2.
M. tuberculosis infection increases lung leukocyte infiltration in obese mice. C57BL/6 mice were fed with the LFD or HFD for 8 weeks and infected with M. tuberculosis by intra-tracheal (it) route. At 4 weeks post-infection (12 weeks of feeding), lungs were evaluated. (a) Total cells (×105/mL) and cell number of (b) neutrophils, (c) monocytes, (d) macrophages, (e) dendritic cells CD11b+, (f) dendritic cells CD103+, (g) lymphocytes CD8+, (h) regulatory T cells Foxp3+, (i) lymphocytes CD4+, (j) IL-17-producing CD4 cells and (k) IFN-γ-producing CD4 cells in the lungs of lean and obese mice infected or not with M. tuberculosis (n = 6–14/group). (l) Correlation between CFU number and CD4+IFN-γ+IL-17− cells (n = 8–11). Data are representative of two independent experiments and are expressed as means ± SD. Bars show the significant difference between groups (p < 0.05).