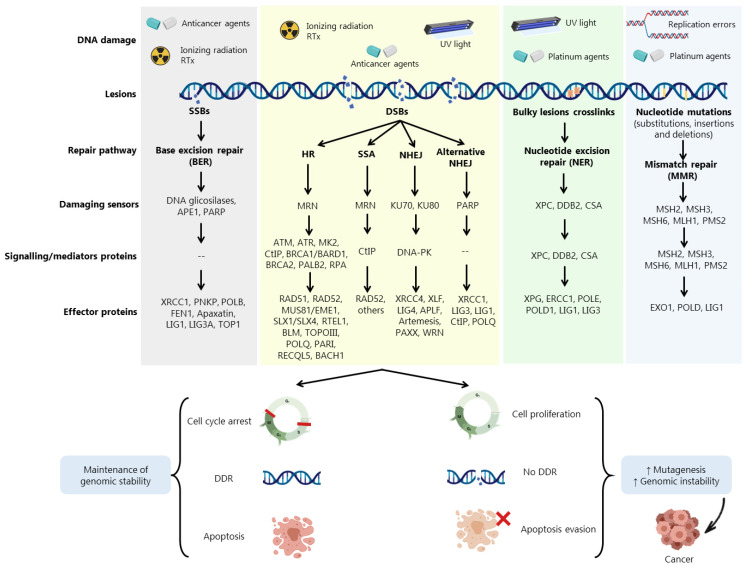
Figure 1.
DNA damage agents and cellular repair pathways. DNA damage repair (DDR) pathways are activated in response to endogenous stresses (e.g., base depurination, deamination and reactive by-products of cellular metabolism) or exogenous exposure to different types of radiation or genotoxic agents. DDR comprises a network of proteins that are either DNA damage sensors, signalling mediators or effector proteins that execute DNA repair. The base excision repair (BER) pathway for single-strand breaks (SSBs), repairs minor DNA changes originated from oxidized or alkylated bases and small base adducts, with poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARP) being the major player. The nucleotide base excision repair (NER) pathway deals with modified nucleotides that change the double helix structure, such as those induced by ultraviolet (UV) light. The mismatch repair (MMR) pathway deals with DNA damage that disturb the DNA helical structure and replication errors as substitution, insertions and deletions. Four different DDR mechanisms are described for double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair: homologous recombination (HR), non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), alternative NHEJ and single-strand annealing (SSA) pathways. Loss or aberrations in DDR proteins allows cell cycle proliferation and evasion of apoptotic events, resulting in increased genomic instability and cancer development. Radiotherapy (Rtx); Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1); MRE11/RAD50/NSB1 (MRN); Xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C (XPC); DNA damage-binding protein 2 (DDB2); Cockayne syndrome group A (CSA); MutS homolog 2, 3 and 6 (MSH2, MSH3 and MSH6); MutL homolog 1 (MLH1); Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM); Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR); Mitogen-activated protein kinase-2 (MK2); C-terminal-binding interacting protein (CtIP); Breast cancer susceptibility 1 and 2 (BRCA1 and BRCA2); BRCA1-associated RING domain (BARD1); Partner and localizer of BRCA2 (PALB2); Replication protein A (RPA); DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK); X-Ray repair cross complementing 1 and 4 (XRCC1 and XRCC4); Polynucleotide kinase 3’-phosphatase (PNKP); DNA polymerase beta (POLB); Flap structure-specific endonuclease 1 (FEN1); DNA ligase 1, 3A and 4 (LIG1, LIG3A and LIG4); DNA topoisomerase 1 and 3 (TOP1 and TOPOIII); Essential meiotic structure-specific endonuclease 1 (EME1); Regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1 (RTEL1); Bloom syndrome protein (BLM); DNA polymerase theta (POLQ); PCNA-associated recombination inhibitor protein (PARI); RecQ like helicase 5 (RECQL5); BRCA1-associated C-terminal helicase (BACH1); XRCC4-like factor (XLF); Aprataxin and PNKP like factor (APLF); Werner syndrome helicase (WRN); Xeroderma pigmentosum group G (XPG); Excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1); DNA polymerase epsilon (POLE); DNA polymerase Delta 1 (POLD1); Exonuclease 1 (EXO1); DNA polymerase delta 1 (POLD).