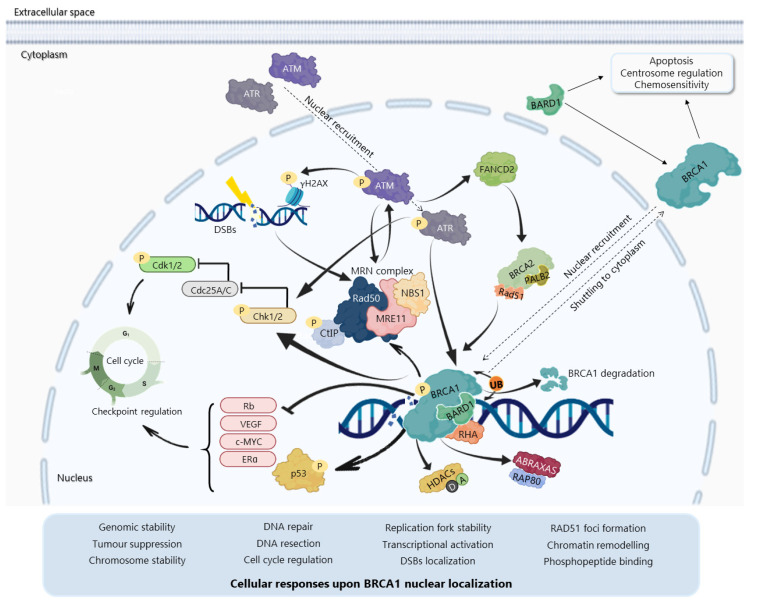
Figure 3.
BRCA1 localization and molecular functions upon DNA damage. DNA damage activates the MRN complex (consisting of MRE11, meiotic recombination 11 homolog A; NBS1, Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1; and RAD50), which phosphorylates and recruits ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM). Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) is also recruited to damaged sites during replication stress. DNA damage can also directly activate ATM/ATR, which can phosphorylate/activate several proteins as checkpoint kinases 1 and 2 (Chk1/2), histone H2AX (γH2AX) and BRCA1. Phosphorylated BRCA1 concentrates in focal areas of DNA damage. At nuclear foci, the BRCA1/BRCA1-associated RING domain (BARD1) heterodimer participates in several molecular mechanisms as DNA repair, cell cycle regulation and transcriptional activation, in association with protein binding partners as MRN complex proteins, C-terminal-binding interacting protein (CtIP), BRCA2/Partner and localizer of BRCA2 (PALB2), RAD51, BRCA1-associated C-terminal helicase (BACH1), BRCA1 A complex subunit (ABRAXAS), receptor-associated protein 80 (RAP80), histone deacetylases (HDACs), RNA helicase A (RHA), among others. The BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimer ubiquitinates several proteins, including BRCA1 and BARD1 although with no degradation by auto-ubiquitination, resulting in increased BRCA1 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. BARD1 phosphorylation abolishes the heterodimer E3 ligase activity. BRCA1-BARD1 hetero-dimerization results in BRCA1 nuclear translocation and retention, while disruption of this complex leads to BRCA1 shuttling to cytoplasm, where BRCA1 influences apoptosis, chemosensitivity and centrosome regulation. Phosphorylation (P); Ubiquitination (Ub); Acetylation (A); Deacetylation (D); Cell division control protein 25 A/C (Cdc25A/C); Estrogen receptor (ER); Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); Fanconi anemia group D2 (FANCD2); Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 and 2 (cdk1/2); Retinoblastoma (Rb).