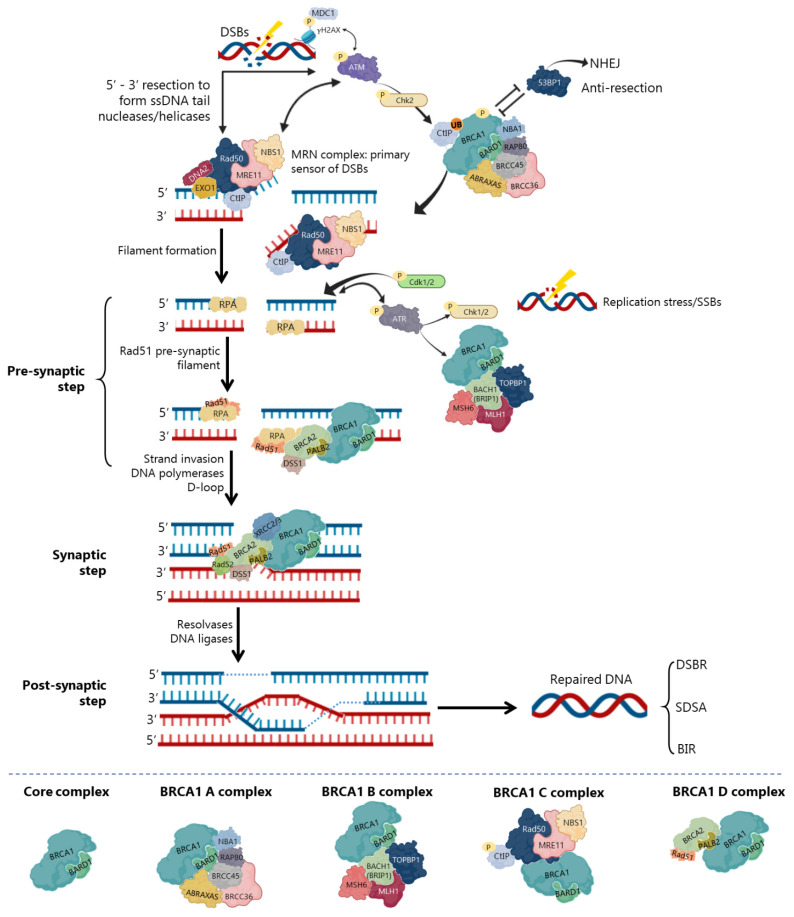
Figure 4.
Double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair by homologous recombination (HR). DNA end resection occurs in the primary steps, a process that leads to nucleolytic degradation of DSBs 5′-ending strands to generate a 3′-end single stranded DNA (ssDNA). MRE11/RAD50/NSB1 (MRN) complex is the first to be recruited to DSBs sites, competing with Ku70/80 from non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway. MRN complex phosphorylates ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and recruits it to DSBs sites, leading to its auto-phosphorylation and phosphorylation of MRN complex. ATM phosphorylates checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2) and the histone H2AX (γH2AX), recruiting the mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1), which enhances ATM phosphorylation and promotes MRN and BRCA1 A complexes recruitment to damage sites. p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1) antagonizes BRCA1 in DSBs resection. Together with C-terminal-binding interacting protein (CtIP) (phosphorylated by MRN, ATM, cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) and ubiquitinated by BRCA1), the MRN complex initiates DSBs resection to expose ssDNA with 3′ ends that undergo strand invasion into a homologous duplex (red), promoting HR. Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) is the primary sensor of replication stress (stalling of replication forks or formation of SSBs), which phosphorylation activates Chk1 and Chk2 and it is recruited to ssDNA sites. ssDNA tails are coated by replication protein A (RPA) followed by the formation of a D-loop structure through RAD51 load on the ssDNA. This is mediated by several proteins as BRCA2/Partner and localizer of BRCA2 (PALB2)/DSS1, BRCA1/BRCA1-associated RING domain (BARD1) and RAD51 cofactors, which allows RAD51 microfilaments formation and subsequent 3′-end strand invasion into the homologous DNA template and D-loop formation. The strand displaced by synthesis (red) anneals to the other resected end of the DSB (blue). To complete the HR process, the newly synthesized strand can dissociate to anneal to the other end. Different outcomes are possible, namely formation of Holliday junctions through DSBs repair (DSBR), synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) and break-induced DNA replication (BIR). Ubiquitination (UB); Phosphorylation (P); Exonuclease 1 (Exo1); DNA helicase/endonuclease 2 (DNA2); DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 (TOPBP1); BRCA1 A complex subunit (ABRAXAS); BRCA1-associated C-terminal helicase (BACH1); MutL homolog 1 (MLH1); MutS homolog 6 (MSH6); BRCA1/BRCA2-Containing Complex Subunit 36 (BRCC36) and BRCC45; Receptor-associated protein 80 (RAP80); X-Ray repair cross complementing 2 (XRCC2) and XRCC3.