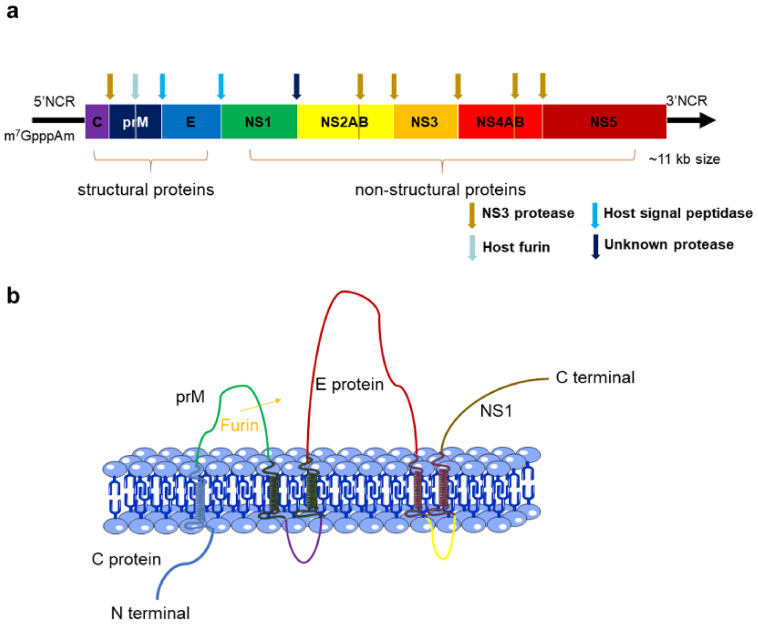
Figure 1.
(a) The long open reading fame (ORF) of flavivirus genome which encodes a polyprotein. The polyprotein is cleaved into 10 proteins by proteases. Capsid protein (C protein), pre-membrane protein (prM protein), and envelope protein (E protein) are structural proteins, whereas the remaining seven are non-structural proteins. There are cleavage sites between proteins, among which the sites indicated by brown arrows can be cleaved by viral proteases, and the sites indicated by blue arrows are the cleavage sites of host proteases. In addition, there is a cap structure at the 5-terminal. (b) Association of the structural proteins of flavivirus. There is a furinase site between prM protein and C protein. In the process of virus transportation to the Golgi body or after virus entry into the Golgi body, the prM is cleaved by furin at this furinase site in the host cell, making the virus particles mature and infectious.