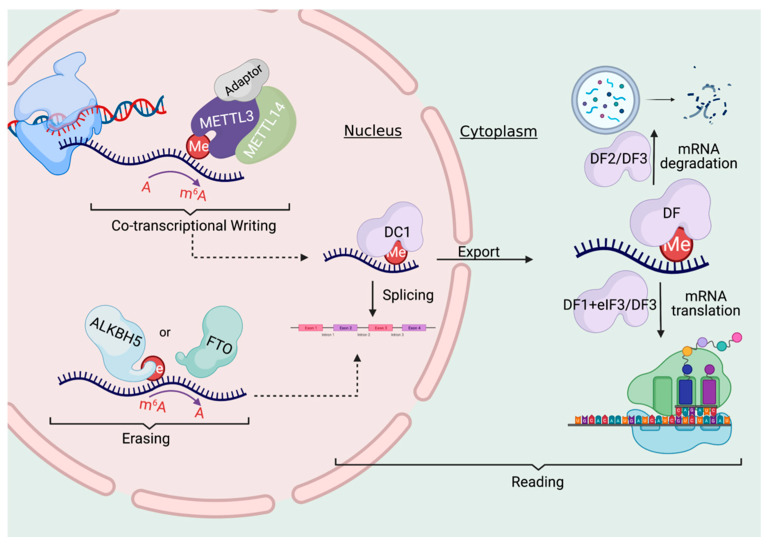
Figure 1.
METTL3 catalyzes m6A methylation (Me) co-transcriptionally within the nucleus which is facilitated by its interacting partner, METTL14, and a number of adaptor proteins that enhance its activity. A modification upon a mRNA derives in large part by the effects of reader proteins such as the YTH domain-containing RNA binding proteins, and ultimately may lead to mRNA splicing, export, degradation, or translation. For example, while YTHDC1 (DC1) exists in the nucleus to promote nuclear export, YTHDF readers can preferentially promote degradation (i.e., YTHDF2, or “DF2”) or translation (i.e., YTHDF1 and YTHDF3, or “DF1” and DF3” here). Alternatively, m6A can also be demethylated by ALKBH5 and FTO in the nucleus.