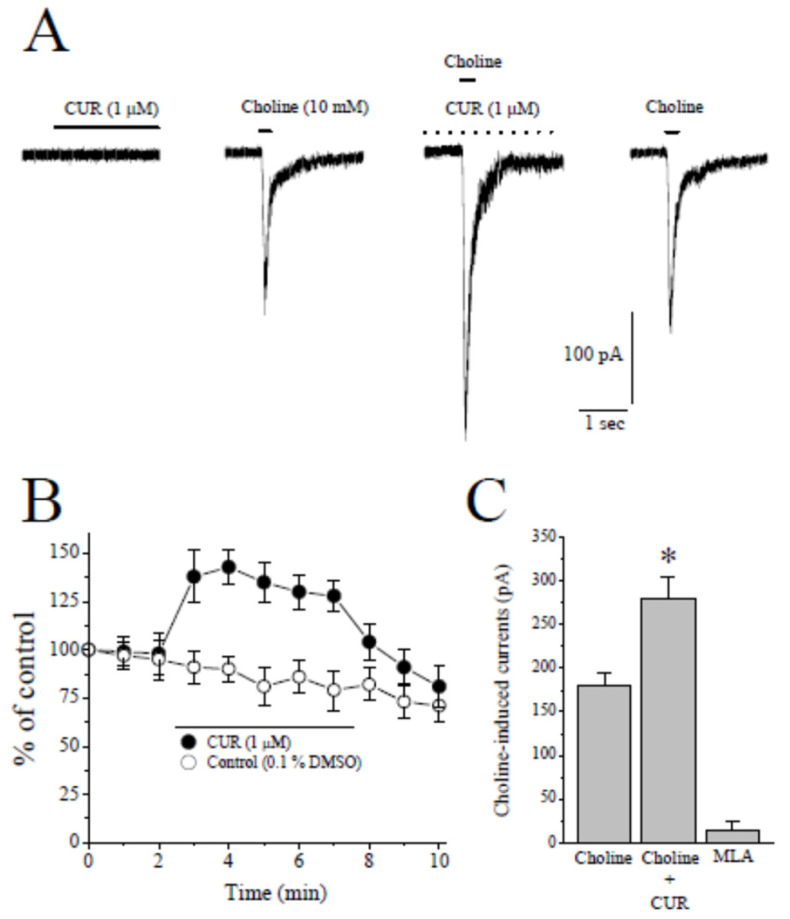
Figure 2.
The effect of curcumin on choline-induced ion currents recorded in CA1 area stratum radiatum interneurons of rat hippocampal slices. (A) Recordings of holding current in the presence of curcumin for 30 s (on the left), choline-induced currents before (control, second panel from left), during (5 min of curcumin) and after (2 min of recovery) the bath application of 1 µM curcumin in hippocampal interneurons. Choline application was represented with a short solid bar on top of the current traces. The dashed line indicates continuing bath application of curcumin. (B) Time-course of the effect of vehicle (0.1% DMSO; open circles) and curcumin (1 µM; filled circles) on the peaks of the Choline-induced currents. Each data point represents the normalized mean ± S.E.M. of five to seven experiments. The duration of drug application is indicated by the horizontal bar in the figure. (C) Summary of the effects of curcumin and methyllycaconitine on the peak amplitudes of choline induced currents. Bars represent the means ± S.E. of four to eight experiments (* p < 0.05 vs. control; ANOVA). MLA, methyllycaconitine.