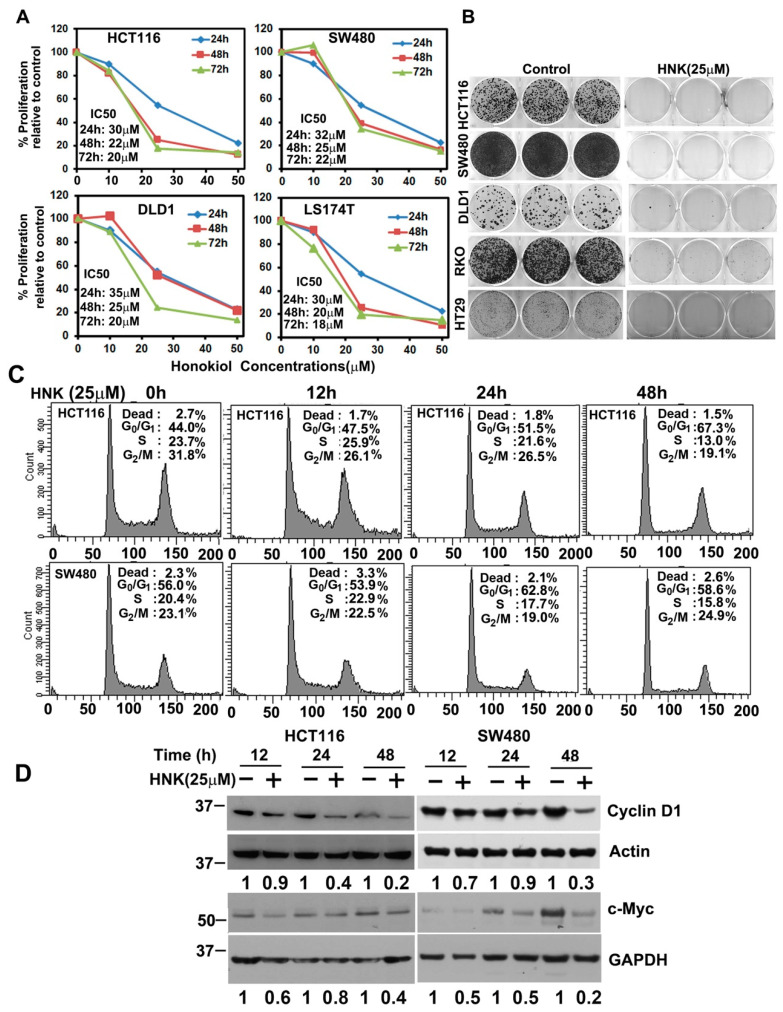
Figure 1.
Honokiol (HNK) inhibits colon cancer cell growth. (A) HCT116, SW480, DLD1, and LS174T cells were incubated with increasing doses of HNK (0–50 μM), and cell proliferation was determined for up to 72 h. HNK treatment resulted in a significant dose- and time-dependent decrease in cell proliferation in all four cell lines when compared with the controls. (B) Cells were incubated with 25 µM HNK for 48 h and subsequently allowed to grow and form colonies in regular media. HNK treatment inhibited colony formation. (C) Cell cycle analysis. HCT116 and SW480 cells were treated with 25 µM HNK for up to 48 h and then examined by flow cytometry following propidium iodide staining for DNA content. HNK treatment induced G0/G1 arrest. (D) Lysates from cells incubated with 25 µM HNK for up to 48 h were analyzed by Western blotting for cyclin D1 and c-Myc expression. HNK inhibits the expression of both cyclin D1 and c-Myc in HCT116 and SW480 cells.