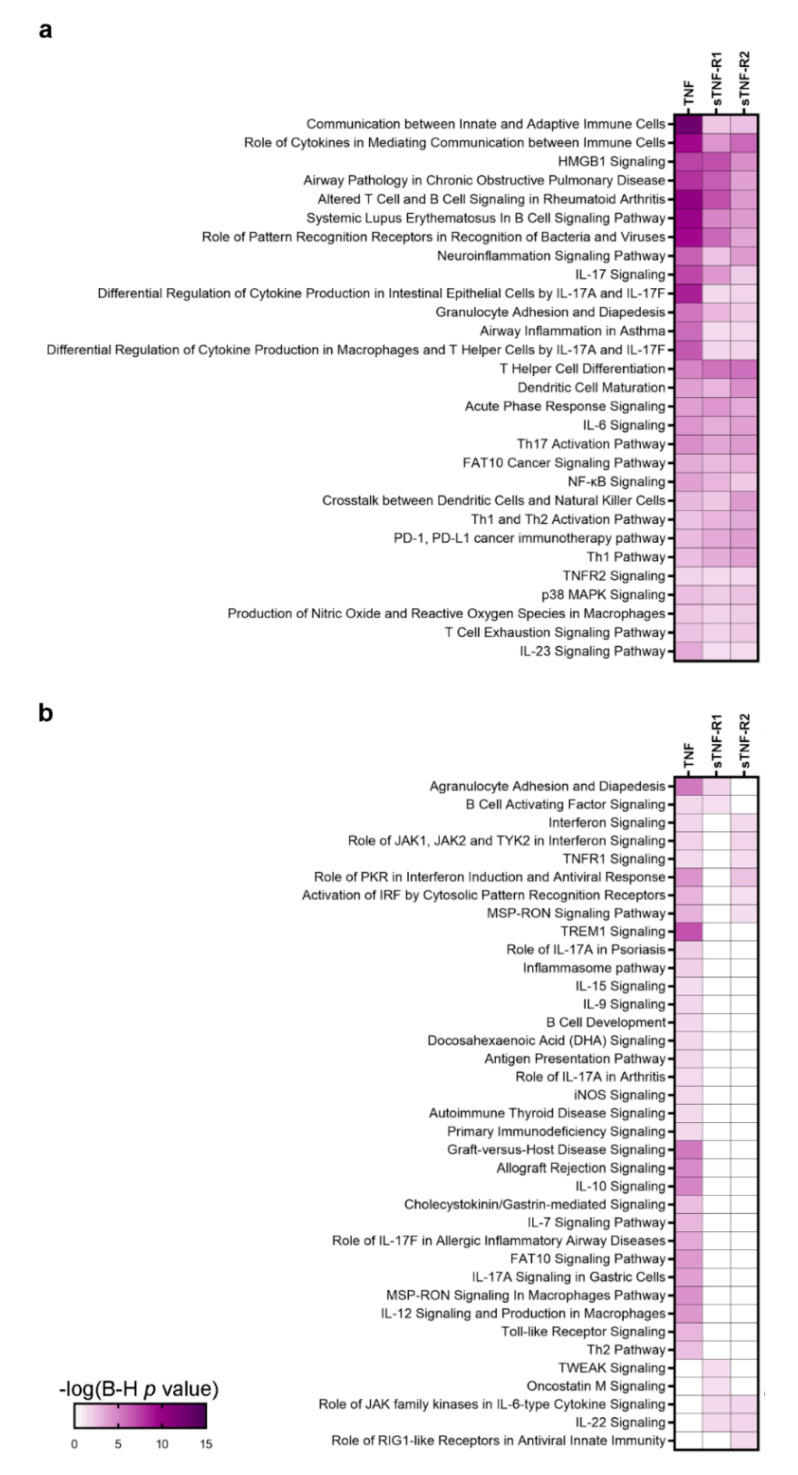
Figure 3.
IPA canonical pathway analysis of TNF, sTNF-R1 and sTNF-R2 molecular patterns. (a) Heatmap of CPs shared among the three profiles pinpointed, in general, a stronger association between inflammatory pathways and TNF profile, as compared to sTNF-R1 and sTNF-R2 profiles. Communication between innate and adaptive immune cells, altered T cell and B cell signalling in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in B cell signalling pathway showed lower p-value in the TNF molecular pattern. HMGB1 signalling, and IL-17 signalling were annotated to a similar extent in TNF and sTNF-R1 profiles. The role of cytokines in mediating communication between immune cells, T helper cell differentiation and dendritic cell maturation were the most significant CPs which characterised the sTNF-R2 profile. Other CPs (including acute phase response signalling, IL-6 signalling, Th17 activation pathway, Th1 and Th2 activation pathway, PD-1, PD-L1 cancer immunotherapy pathway) were shared among the three molecular patterns without remarkable difference in terms of p-value. (b) Heatmap of CPs associated with at least one or two molecular profiles indicated that TNF profile was characterised by the higher number of CPs when compared to the other two molecular patterns. Among them, CPs related to TREM-1 signalling, B cells development and IL-10 signalling were significantly annotated in the TNF profile only. For a comprehensive list of molecules enclosed in each CPs see Supplementary Table S2.