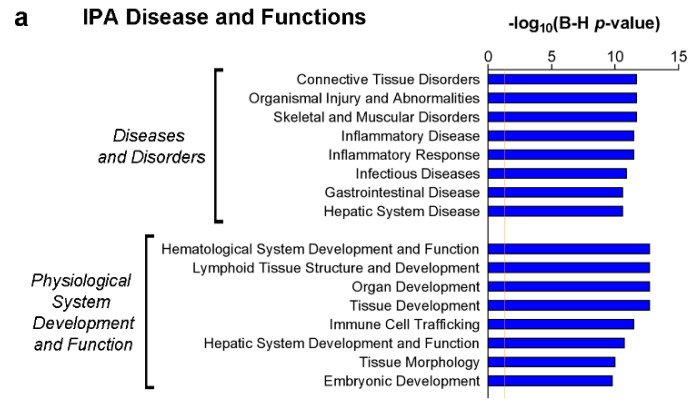
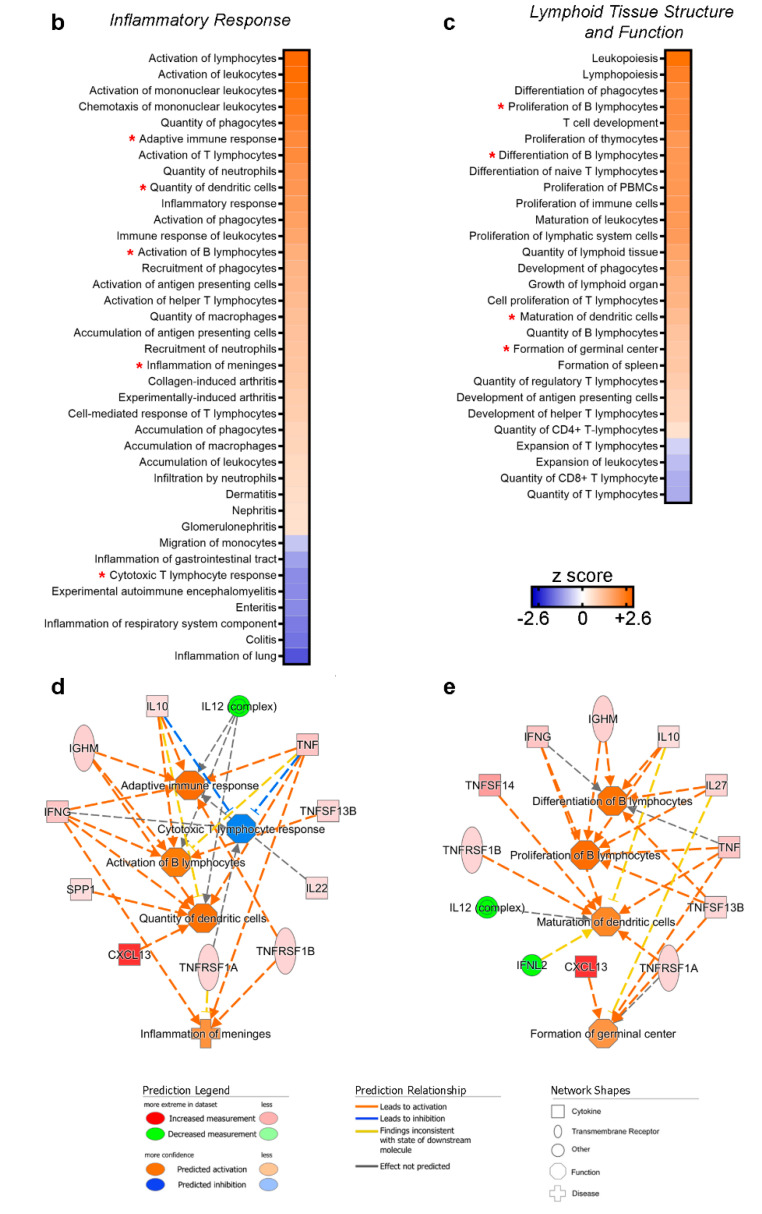
Figure 6.
(a) Inquiry of disease and functions annotations revealed many categories with highly significant B-H corrected p-values related to inflammation (inflammatory response and disease, immunological disease) and immune cells processes (lymphoid tissue structures and development, immune cell trafficking). See Supplementary Table S4 for the complete analysis of disease and function categories. (b,c) Heatmaps of functional annotations encompassed in inflammatory response and lymphoid tissue structure and development from (a). All these functions showed a |z-score| > 0.5; annotations marked by red asterisk were further utilised to generate networks in panel (d,e). For the complete list of the annotations enclosed in the two categories see Supplementary Tables S5 and S6. (d,e) Networks from selected annotations of inflammatory response (d) and lymphoid tissue structures and development categories (e) pinpointed an involvement of adaptive immunity and B cell response; conversely, annotations related to T cell response were associated with negative z-score, predicting an inhibition state. Notably, inflammation of meninges was also found to be activated: this prediction was supported by the increased expression of IFN-γ, TNFRS1B/TNF-R2 and TNF (orange arrows), whereas TNFRS1A/TNF-R1 showed an inconsistent relationship (yellow arrow). Furthermore, the activation state of formation of germinal centre was supported by the increased expression of CXCL13, BAFF/TNFRSF13B and TNF (orange arrows), whereas the upregulation of IL-27 was inconsistent with the prediction (yellow arrow); the effect of the relationship with TNFRSF1A/TNF-R1 could not be predicted (grey arrow).