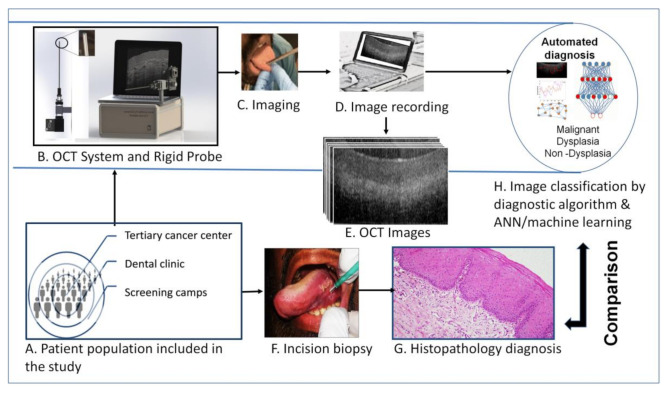
Figure 1.
Study design. The subjects were: (A) recruited from low resource settings (oral cancer screening camps), dental hospitals and tertiary cancer center. (B) A portable Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) system, (C)was used to capture oral mucosal lesion images, after oral physician consultation. The OCT images were recorded in laptop and used for image pre-processing and automated image analysis (D,E). The subjects underwent incision/excision biopsy (if indicated) for histopathological diagnosis (F,G). The OCT images were then analyzed by automated image processing and algorithm/artificial intelligence (H) based classification and compared with histological diagnosis.