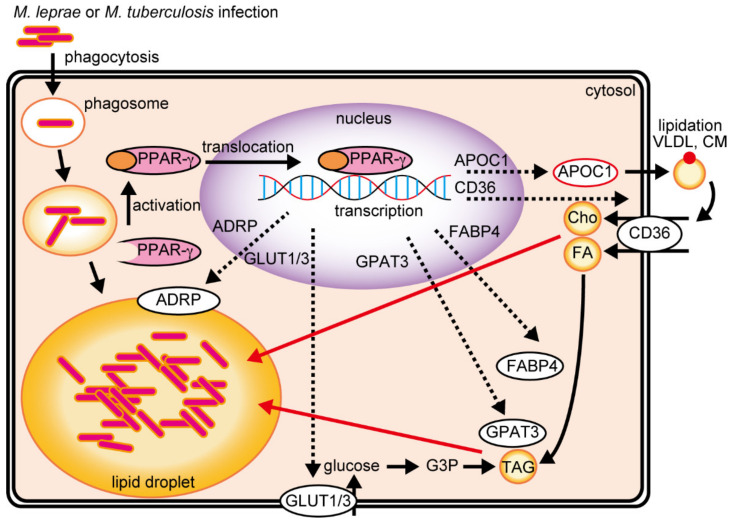
Figure 1.
M. leprae and M. tuberculosis infections activate PPAR-γ to induce lipid droplet formation in the host cell. APOC1 binds to extracellular VLDL cholesterol or CM and is followed by LDL cholesterol uptake via CD36, thus accumulating intracellular cholesterol. Intracellular TAG accumulation is induced by two PPAR-γ-mediated pathways. FABP4 acylates extracellular fatty acids taken up by CD36 and is utilized by GPAT3 for TAG synthesis. GLUT1/3 induces intracellular glucose uptake and is subsequently utilized by GPAT3 for TAG synthesis. APOC1, apolipoprotein C-1; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein; CM, chylomicron; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; FABP4, fatty acid-binding protein 4; FA, fatty acid; TAG, triacylglycerol; GPAT3, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 3; GLUT1/3, glucose transport protein type 1/3.