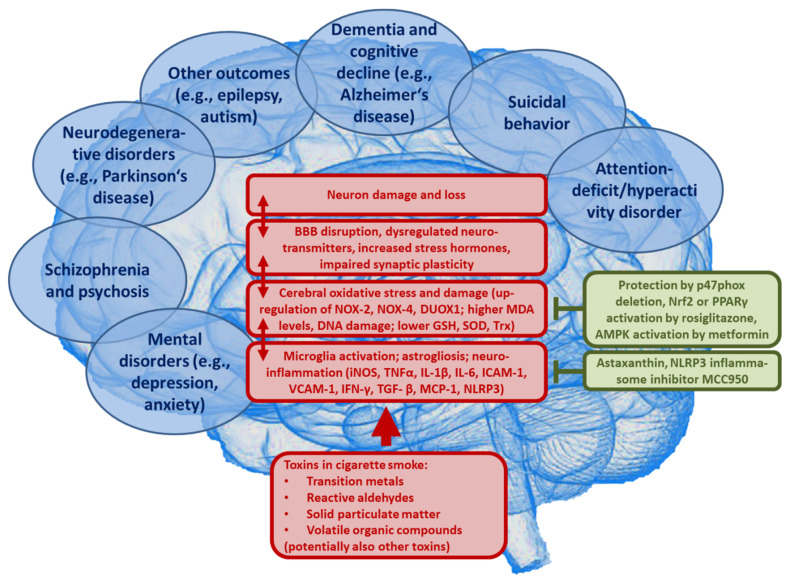
Figure 5.
Proposed concept how the major toxins in cigarette smoke may contribute to neurological complications and neuronal/psychiatric diseases. Uptake of fine particulate matter, heavy/transition metals, reactive aldehydes, volatile organic compounds, and other cigarette smoke toxins leads to neuroinflammation and cerebral oxidative stress by microglia activation, impairing vital pathways in the brain, and initiating pathophysiological processes such as amyloid deposition and neuron damage and loss. BBB, blood-brain barrier; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-1β, interleukin 1beta; IL-6, interleukin 6; NOX-2, NADPH oxidase isoform 2 (phagocytic NADPH oxidase); NOX-4, NADPH oxidase isoform 4; DUOX1, dual oxidase 1; MDA, malondialdehyde; GSH, glutathione; SOD, superoxide dismutase; Trx, thioredoxin; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (CCL2); TGF- β, transforming growth factor beta; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; p47phox, regulatory subunit of NOX-2 and NOX-1; Nrf2, nuclear factor E2 related factor-2; PPAR γ, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase.