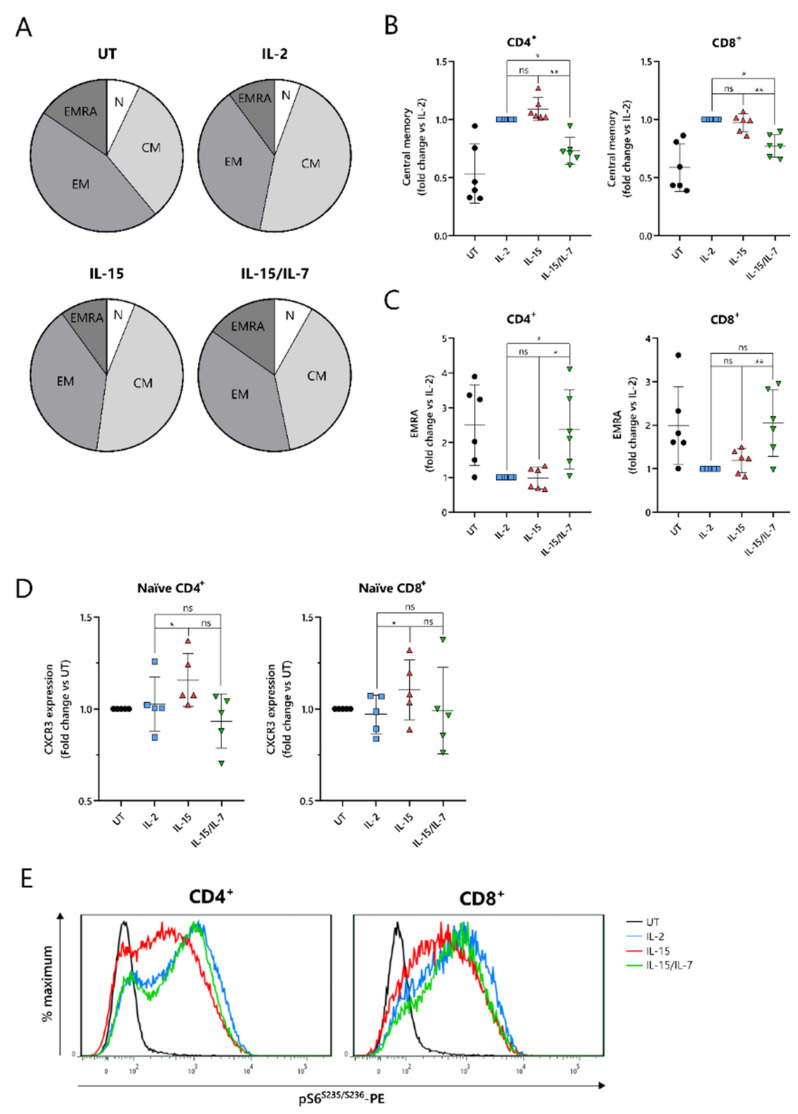
Figure 4.
IL-7 drives a more differentiated memory phenotype in ARI2h BCMA-CARs cultured with IL-15. (A) Pie charts showing a summary of phenotypes of in vitro-expanded CD8+ (UT) and CD8+CAR+ (ARI2hIL-2, ARI2hIL-15, ARI2hIL-15/IL7) T cells. N—naïve (CCR7+CD45RA+), CM—central memory (CCR7+CD45RA−), EM—effector memory (CCR7-CD45RA−), EMRA—effector memory CD45RA+ (CCR7-CD45RA+). n = 6. (B,C) Relative frequency of T cells with a central memory (B) or EMRA (C) phenotype within the CD4+ and CD8+ (UT) or CAR+ CD4+ and CD8+ (ARI2hIL-2, ARI2hIL-15 and ARI2hIL-15/IL-7) cultures, normalized to ARI2hIL-2. (D) CXCR3 expression on naïve-phenotype CD4+ and CD8+ (UT) or CAR+ CD4+ and CD8+ (ARI2hIL-2, ARI2hIL-15 and ARI2hIL-15/IL-7) T cells, based on the MFI of the staining and normalized to UT T cells. E) Phosphorylation of the ribosomal S6 protein on serine 235/serine 236 in UT or CAR+ CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after a 6-hour challenge with ARP-1 cells. Images shown are representative histograms (n = 4). The statistics for panels B–C were performed on raw data. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; ns, not significant.