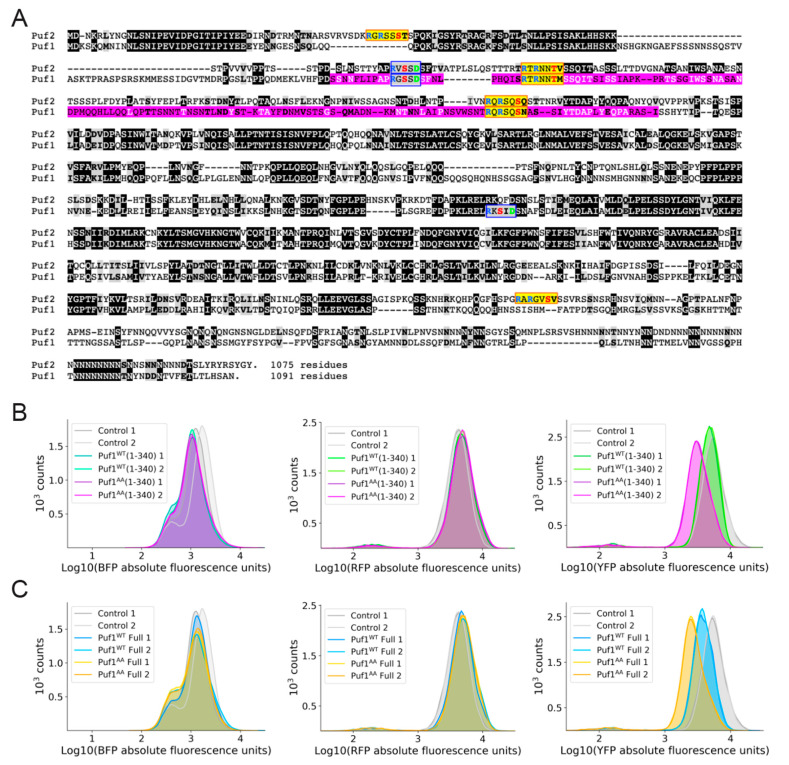
Figure 4.
Absence of Ypk1-mediated phosphorylation enhances transcriptional repression by Puf1. (A) Sequence alignment of Puf1 (bottom) and Puf2 (top). Identities, white letter on a black box; standard conservative substitutions, bold letter in a gray box; consensus Ypk1 phosphorylation sites, yellow boxes; consensus Fpk1 phosphorylation sites, blue boxes; Puf1 fragment (residues 143-295) isolated in initial screen [45], pink shading. (B) FACS analysis of the level of expression of BFP (left panel), RFP (middle panel), and YFP (right panel) for control cultures expressing a Halo tag-λN-BFP fusion (grey peaks; n = 2), cultures expressing the Puf1WT(1-340)-λN-BFP fusion (green peaks; n = 2), and cultures expressing the Puf1AA(1-340-λN-BFP fusion (violet peaks; n = 2). (C) FACS analysis of the level of expression of BFP (left panel), RFP (middle panel), and YFP (right panel) for control cultures expressing a Halo tag-λN-BFP fusion (grey peaks; n = 2), cultures expressing the Puf1WT-λN-BFP fusion (blue peaks; n = 2), and cultures expressing the Puf1AA-λN-BFP fusion (orange peaks; n = 2).