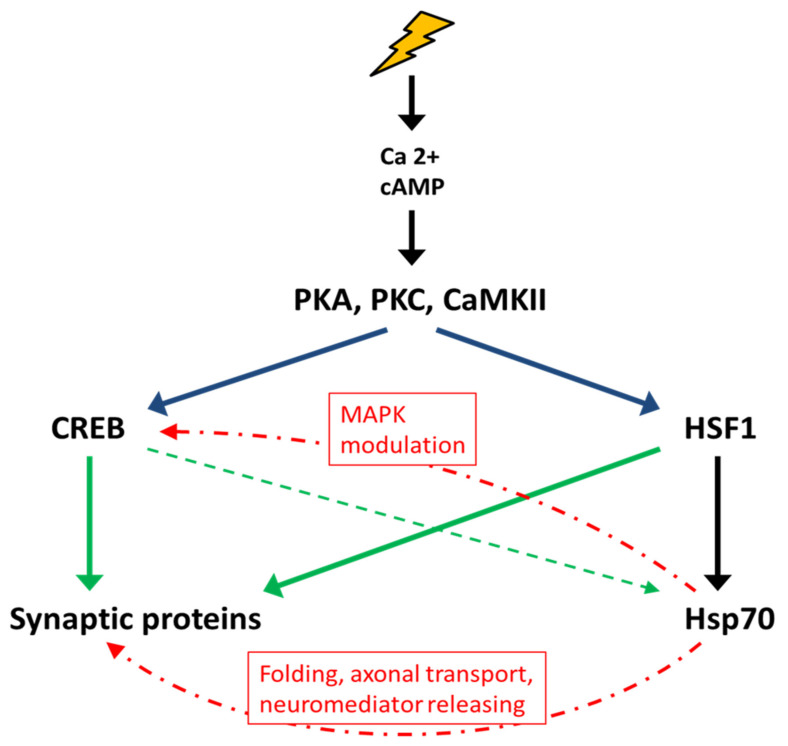
Figure 4.
Interactions between the stress response and memory formation. Stress stimuli lead to an increase in the concentration of calcium and cAMP in the cytosol in CNS cells and the activation of protein kinases PKA, PKC, CaMKII, etc., which are involved in the regulation of the activity of transcription factors, in particular, CREB and HSF1. Both CREB and HSF1 initiate the transcription of genes encoding synaptic proteins and Hsp70. In turn, Hsp70 promotes the folding and transport of synaptic proteins and the release of neurotransmitters, activates the MAPK signaling cascade, and ensures the structural integrity of synapses by interacting with the cytoskeleton.