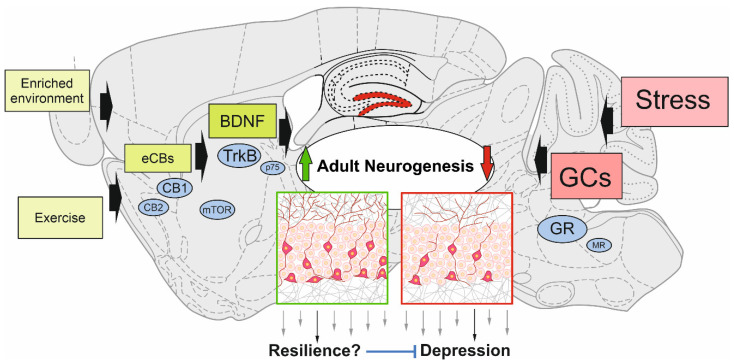
Figure 1.
Schematic view of modulating factors of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Enriched environment, exercise, and molecular players (e.g., endocannabinoids (eCBs) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)) have the potential to upregulate the generation of adult-born neurons in the dentate gyrus. This could confer resilience to the development of depressive-like symptoms through the stress-related decline of adult neurogenesis induced by glucocorticoids (GCs). The main signaling pathways of positive modulators and stress are depicted: cannabinoid receptor type-1 and -2 (CB1; CB2); mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR); tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB); p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75); glucocorticoid receptor (GR); mineralocorticoid receptor (MR).