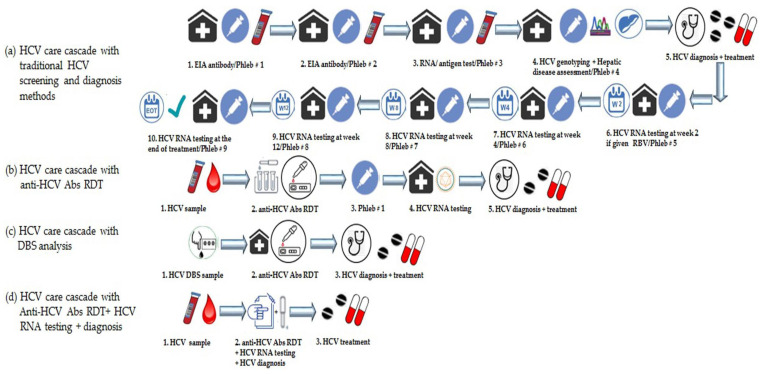
Figure 2.
A schematic illustration deciphering the importance of simplified HCV diagnosis solutions to minimizing steps to infection diagnosis and pursuit a single visit diagnosis than the traditional complicated diagnostic pathways in HCV care cascade. (a) elaborates the traditional HCV screening and diagnostic procedures in a care cascade which requires 10 single visits, 9 phlebotomies, HCV genotyping assessment, and liver disease staging for disease assessment from HCV screening to infection cure [48]. (b) demonstrates the anti-HCV antibodies (Abs) rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) from HCV screening to treatment which requires four single visits from screening to treatment, one phlebotomy for active infection confirmation, and skipping HCV genotype assessment provided that the patient is prescribed to pan-genotypic DAAs regimens for treatment; however, liver disease staging for disease assessment may require for determining cirrhosis status of the patient (i.e., present or absent; compensated or decompensated cirrhosis), for treatment initiation, treatment type, and length of HCV treatment for HCV GT-3 infected patients. (c) shows the dried blood spot (DBS) sample testing by anti-HCV Abs RDTs and the patient receives diagnosis within two visits. (d) depicts the anti-HCV Abs RDT, HCV RNA POC test for active viremic infection confirmation, infection diagnosis, and the patient receiving pan-genotypic DAA treatment in a single visit. The prospect of this illustration reflects the importance of a simplified HCV diagnostic pathway (i.e., either choosing (b), (c), or (d) rather than the traditional (a) to overcome the obstacles of multiple visits, phlebotomies, and increased time which potentially loses many patients during HCV screening to diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and cures follow-ups in real-world clinical settings [48]. Simplified HCV diagnostics are also helpful to remove the hurdles to scale-up HCV diagnosis in HCV vulnerable populations (e.g., PWIDs, IUDs, MSM) where poor venous access is always a major challenge to draw a venous blood sample [48].  = central lab,
= central lab,  = phlebotomy,
= phlebotomy,  = sample,
= sample,  = HCV RNA testing,
= HCV RNA testing,  = hepatic disease assessment,
= hepatic disease assessment,  = diagnosis,
= diagnosis,  = treatment,
= treatment,  = RDT,
= RDT,  = DBS,
= DBS,  = RDT + HCV RNA + diagnosis,
= RDT + HCV RNA + diagnosis,  = treatment week,
= treatment week,  = end of treatment,
= end of treatment,  = HCV cure,
= HCV cure,  = linkage to care,
= linkage to care,  = testing
= testing  = mortality
= mortality  = HCV genotyping. RDT = rapid diagnostic tests, Ab = Antibody, DBS = dried blood spot, POC = point-of-care, RBV = ribavirin, Phleb = phlebotomy.
= HCV genotyping. RDT = rapid diagnostic tests, Ab = Antibody, DBS = dried blood spot, POC = point-of-care, RBV = ribavirin, Phleb = phlebotomy.