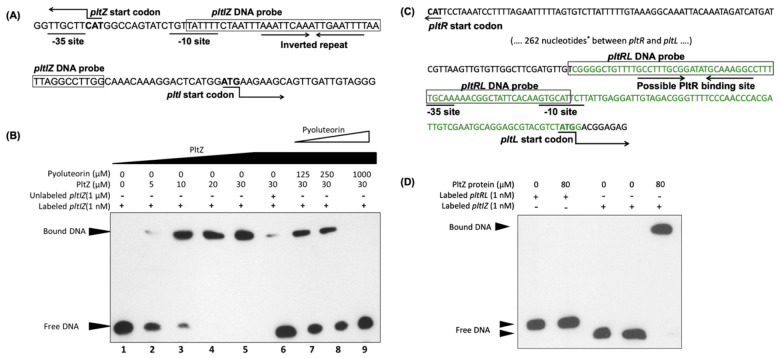
Figure 5.
PltZ binds to the pltI-pltZ intergenic region. (A) Intergenic region between pltI and pltZ in the chromosome of Pf-5. The predicted -10 and -35 sites of pltI promoter and an inverted repeat are shown. (B) EMSA binding assay of interactions between PltZ protein, the pltIZ DNA probe (shown in (A)), and the pyoluteorin compound. The interactions were performed in 20 μL reactions at 25 °C. Lane 1 serves as a control which contains only labeled pltIZ DNA probe; lanes 2 to 5 contain labeled pltIZ probe and different concentrations of PltZ protein; lane 6 contains unlabeled pltIZ DNA fragment to compete for PltZ protein; lanes 7 to 9 contain different concentrations of pyoluteorin to test if this compound releases the pltIZ probe from its binding complex with PltZ. (C) Intergenic region between pltR and pltL in the chromosome of Pf-5. The predicted −10 and −35 sites of pltL promoter and a possible PltR binding site similar to the lys box identified in P. aeruginosa M18 [22] are shown. *: 262 nucleotides between the indicated pltR and pltL intergenic region are not shown. The DNA fragment labeled with green color was fused with a promoterless gfp to monitor the promoter activity of pltL in the reporter construct pL-gfp that was made previously [32] and used in this study (Figure 1C). (D) EMSA binding assay of interactions between PltZ protein and the pltRL DNA probe (shown in (C)). The pltIZ DNA probe used in (B) served as a positive control. The experiments were repeated at least two times.